HS Class 12 Biology Solved Question Paper 2022 – Complete Solution| Assam Eduverse
Introduction
HS Class 12 Biology solved question paper 2022 is a crucial resource for students preparing for the Higher Secondary Biology examination. The HS Class 12 Biology solved question paper 2022 helps students understand the exam pattern, marking scheme, and important questions. By practising the HS Class 12 Biology solved question paper 2022, students improve accuracy and confidence.
Many students find Biology lengthy, but the HS Class 12 Biology solved question paper 2022 makes preparation systematic and exam-focused. Regular revision of the HS Class 12 Biology solved question paper 2022 strengthens concepts and improves diagram-based answers. Solving the HS Class 12 Biology previous year question paper helps identify repeated questions.
This HS Class 12 Biology solved question paper 2022 is prepared strictly as per the ASSEB syllabus. Practising AHSEC Class 12 Biology solved questions and the ASSEB HS 2nd Year Biology question paper ensures better performance. Assam Eduverse provides the HS Class 12 Biology solved question paper 2022 to help students score maximum marks.
Previous Year Solved Question Paper for HS Class 12 Biology 2022
Biology (Theory) – H.S. Final Exam 2022
Complete Answers
PART – I (BOTANY)
Q.1 What is Plasmid? (1)
Answer:A plasmid is a small, circular, double-stranded extrachromosomal DNA molecule found in bacteria that can replicate independently of chromosomal DNA.
Q.2 Name the plant body where bisexual and both unisexual male and female flowers are present. (1)
Answer: Cucurbita (Pumpkin).
Q.3 Write full form of VAM. (1)
Answer: Vesicular Arbuscular Mycorrhiza.
Q.4 Who proposed Mutation theory? (1)
Answer: Hugo de Vries proposed the Mutation theory.
Q.5 What is biogas? (2)
Answer: Biogas is a mixture of gases, mainly methane, produced by anaerobic decomposition of organic waste like cow dung by microorganisms and used as a fuel.
Q.6 Name two antibiotics produced from fungi. (1+1 = 2)
Answer: Penicillin and Cephalosporin.
Q.7 How is DNA isolated in purified form from a bacterial cell? (2)
Answer: Bacterial cells are lysed using enzymes and detergents, proteins are removed by protease treatment, and DNA is precipitated using cold alcohol to obtain purified DNA.
OR
What is recombinant DNA? List the tools of Genetic Engineering. (2)
Answer: Recombinant DNA is DNA formed by combining DNA from two different organisms.
Tools of genetic engineering include restriction enzymes, vectors, DNA ligase and host cells.
Q.8 What is triple fusion? Name the nuclei involved in the process. (1+1 = 2)
Answer: Triple fusion is the fusion of one male gamete with two polar nuclei during fertilization in angiosperms.
The nuclei involved are one male nucleus and two polar nuclei.
OR
What is polyembryony in angiosperms? Write its importance. (1+1 = 2)
Answer: Polyembryony is the occurrence of more than one embryo in a single seed.
It is important in producing disease-free and vigorous plants.
Q.9 What is totipotency of the cell? Write its importance in plant science. (1+1 = 2)
Answer: Totipotency is the ability of a single plant cell to develop into a complete plant.
It is important for plant tissue culture and micropropagation.
Q.10 Explain briefly (any two): (2+2 = 4)
(i) Gene Gun
Answer: Gene gun is a method of gene transfer used mainly in plants, in which microscopic metal particles such as gold or tungsten are coated with DNA and then shot at high speed into plant cells or tissues. The DNA enters the cell and integrates with the host genome, enabling the expression of the introduced gene.
(ii) Gene Cloning
Answer: Gene cloning is the process of producing multiple identical copies of a specific or desired gene. It involves inserting the gene into a suitable vector such as a plasmid, which is then introduced into a host organism like bacteria. As the host cell multiplies, the inserted gene is replicated, allowing large-scale production and study of the gene.
Q.11 Write the scientific names with their utilities (any three): (1½×3 = 3)
(i) Tobacco
Answer: Nicotiana tabacum — It is mainly used in the cigarette, cigar, and tobacco industry. It is also used for extracting nicotine, which is employed in insecticides and certain medicinal preparations.
(ii) Tulsi
Answer: Ocimum sanctum — Tulsi is widely used for medicinal purposes due to its antibacterial, antiviral, and immunity-boosting properties. It also holds great religious significance and is commonly used in traditional rituals and herbal remedies.
(iii) Jute
Answer: Corchorus capsularis — Jute is an important fibre crop used for making ropes, gunny bags, carpets, mats, and eco-friendly packaging materials. It is valued for its strength and biodegradability.
Q.12 How do biofertilizers enrich the fertility of the soil? (2)
Answer: Biofertilizers enrich soil fertility by increasing the availability of essential nutrients to plants. They fix atmospheric nitrogen, solubilize phosphates, and enhance soil microbial activity, which improves soil structure, nutrient cycling, and overall soil health.
Q.13 Describe the development of female gametophyte in angiosperms. (3)
Answer: In angiosperms, the female gametophyte or embryo sac develops from a diploid megaspore mother cell present in the ovule. The megaspore mother cell undergoes meiosis to form four haploid megaspores, out of which three degenerate and only one remains functional. The functional megaspore undergoes three successive mitotic divisions to produce an eight-nucleate structure, which organizes into a seven-celled embryo sac consisting of one egg cell, two synergids, three antipodal cells, and a central cell with two polar nuclei.
OR
Explain any three outbreeding devices. (3)
Answer: Three outbreeding devices are-
- Dichogamy: It refers to the difference in the timing of maturity of stamens and pistil in a flower, which prevents self-pollination. It may be of two types—protandry (stamens mature first) and protogyny (pistil matures first).
- Herkogamy: It is the physical or spatial separation of anther and stigma within the same flower, which reduces the chances of self-pollination.
- Self-incompatibility: It is a genetically controlled mechanism in which pollen from the same plant or genetically similar plants fails to fertilize the ovule, thereby preventing self-pollination and promoting cross-pollination.
Q.14 Write briefly on Modern Synthetic Theory of Evolution. (4)
Answer: The Modern Synthetic Theory of Evolution explains evolution as a gradual and continuous process resulting from the combined action of genetic variation, mutation, recombination, natural selection, genetic drift, and gene flow. Genetic variations arise due to mutations and recombination during sexual reproduction, providing raw material for evolution. Natural selection preserves favourable variations, while genetic drift and gene flow bring changes in gene frequencies within populations. Together, these factors lead to adaptation, speciation, and evolutionary change over long periods of time.
OR
Describe the factors involved in organic evolution. (4)
Answer: Organic evolution is brought about by several factors that act together over long periods of time to produce evolutionary changes in organisms. Mutation creates sudden heritable variations in organisms and provides raw material for evolution. Recombination during sexual reproduction reshuffles genes and produces new gene combinations, increasing variation within a population. Natural selection favors organisms with beneficial variations, allowing them to survive and reproduce more successfully. Genetic drift causes random changes in gene frequencies, especially in small populations, while isolation prevents interbreeding between populations, leading to the formation of new species.
Q.15 Define Biotechnology. Write briefly on the main aims of biotechnology. (1+4 = 5)
Answer: Biotechnology is the application of biological organisms, cells, enzymes, or biological systems to develop or produce useful products and processes for human welfare.
The main aims of biotechnology include improving crop yield and quality through genetic engineering, producing medicines such as vaccines, antibiotics, and hormones, protecting the environment through bioremediation and waste management, and developing genetically modified organisms with desirable traits for agriculture, industry, and healthcare.
OR
Write an account on biotechnological applications in medicine. (5)
Answer: Biotechnology plays a vital role in the field of medicine by improving the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of diseases. One major application is the production of recombinant insulin, vaccines, and antibiotics using genetically engineered microorganisms, which ensures purity and large-scale availability. Biotechnology is also used in the development of recombinant drugs such as growth hormones and interferons for treating various disorders.
Another important application is gene therapy, where defective genes are replaced or corrected to treat genetic diseases. Biotechnology also aids in the early diagnosis of diseases through techniques like ELISA and PCR, helping in accurate and timely detection. Overall, biotechnological applications have greatly advanced modern medicine and improved human health.
PART – II (ZOOLOGY)
1. Fill in the blanks : (any two) (½×4 = 2)
(a) The main function of interstitial cells of seminiferous tubules is secretion of male hormone testosterone.
(b) Thomas Hunt Morgan proposed that nuclei are the bearers of hereditary characters.
(c) The AUG codon is called start codon / initiation codon.
(d) Elephantiasis is caused by Wuchereria bancrofti.
(e) Greenhouse effect is mainly caused due to carbon dioxide (CO₂).
Q.2 Answer any two: (1×2 = 2)
(a) What is Template strand?
Answer: Template strand is the DNA strand that guides synthesis of mRNA during transcription.
(b) Define Test cross.
Answer: Test cross is a cross between an organism with dominant phenotype and a homozygous recessive individual.
Q.3 Answer any four: (2×4 = 8)
(a) What is Menstrual cycle? Which hormones control it?
Answer: Menstrual cycle is the monthly cycle of changes in the female reproductive system’
Menstrual cycle is controlled by FSH, LH, estrogen and progesterone.
(b) What is Point mutation? Give one example.
Answer: Point mutation is a change in a single nucleotide base. Example: Sickle-cell anaemia.
(c) What is Adaptive radiation? Give one example.
Answer: Adaptive radiation is evolution of different species from a common ancestor.
Example: Darwin’s finches.
(d) Define Ecological pyramid with one example.
Answer: Ecological pyramid represents trophic levels graphically. Example: Pyramid of energy.
Q.4 Write differences between (any two): (2+2 = 4)
(a) Homozygous and Heterozygous
Answer: Differences between Homozygous and Heterozygous are:
- Homozygous condition refers to the presence of two identical alleles of a gene for a particular trait; whereas heterozygous condition refers to the presence of two different alleles of the same gene.
- Homozygous individuals produce only one type of gamete; on the other hand, heterozygous individuals produce two types of gametes.
(b) Vaccination and Immunisation
Answer: Differences between Vaccination and Immunisation are:
- Vaccination is the process of administering a vaccine containing weakened or killed pathogens into the body; whereas immunisation is the process by which the body develops immunity against a disease.
- Vaccination is the cause of immunity and is an artificial method; on the other hand, immunisation is the result of vaccination or natural exposure and involves the production of antibodies and memory cells.
Q.5 Draw a labelled diagram of T.S. of ovary. (3)
Answer: 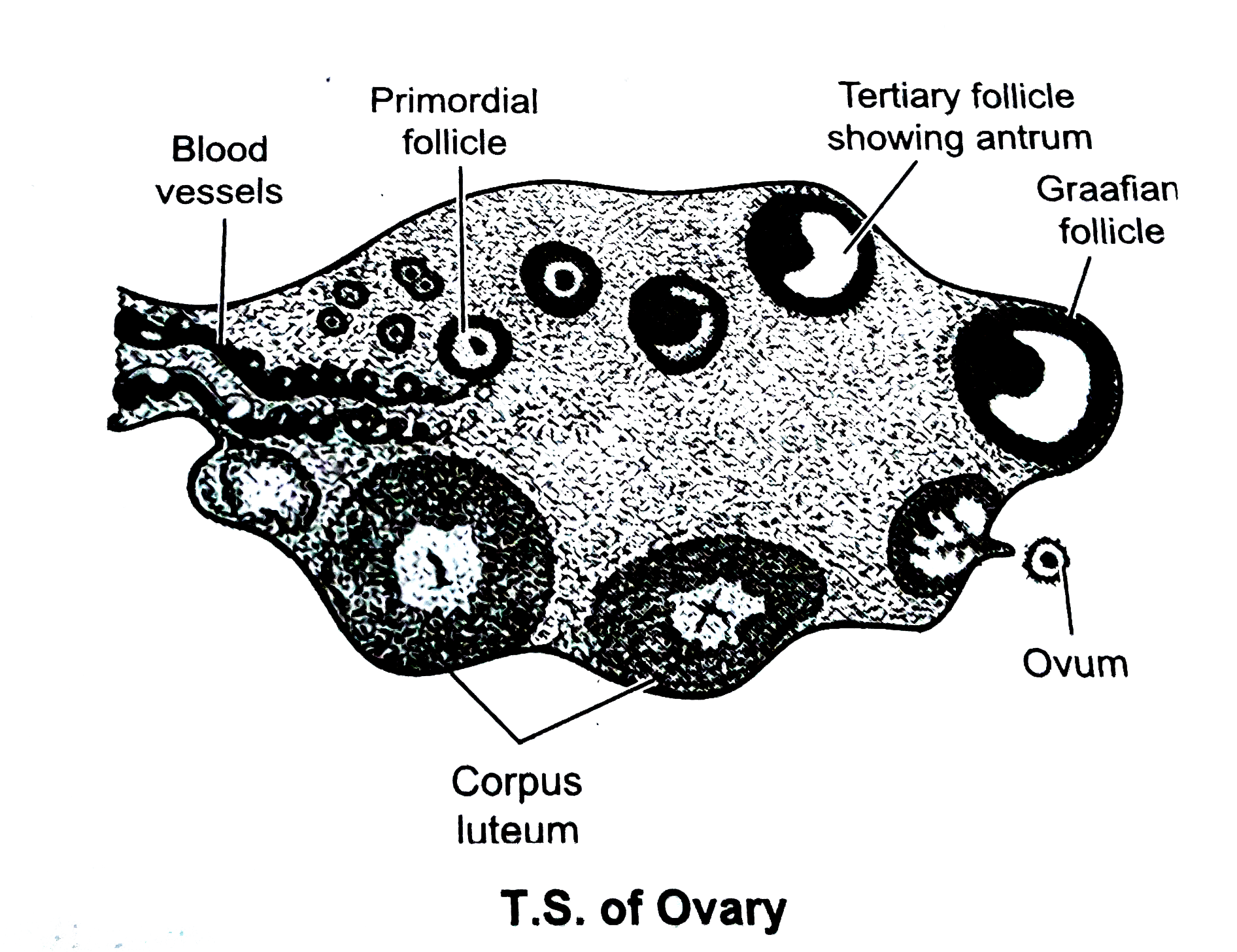
OR
Draw a labelled diagram of double helical structure of DNA. (3)
Answer:
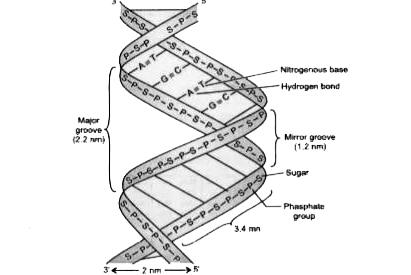
Q.6 What are sexually transmitted diseases? Mention causes. (1+2 = 3)
Answer: Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) are diseases that are transmitted from one person to another mainly through sexual contact with an infected individual. The causes of STDs include infection by bacteria, viruses, protozoa, and sometimes fungi, which enter the body during unsafe sexual practices and spread through body fluids.
OR
Mention the effects of drugs and alcohols. (3)
Answer: Drugs and alcohol have several harmful effects on individuals and society. They cause addiction and dependence, making it difficult for individuals to control their consumption. Prolonged use leads to damage of vital organs such as the liver, brain, heart, and kidneys, and may result in serious health problems. Drugs and alcohol also cause mental disorders, impaired judgment, and behavioral changes, leading to social problems such as family conflicts, accidents, crime, and loss of productivity.
Q.7 Write the salient features of Human Genome. (3)
Answer: The human genome consists of about 3 billion base pairs of DNA present in 23 pairs of chromosomes. It contains approximately 20,000–25,000 genes that control various structural and functional characteristics of the human body. A large portion of the human genome is non-coding DNA, which does not code for proteins but plays important roles in regulation, evolution, and genetic stability.
OR
Write reasons for loss of biodiversity. (3)
Answer: Loss of biodiversity occurs due to several natural and human-induced factors. Habitat loss and destruction caused by deforestation, urbanization, and industrialization is a major reason for the decline of plant and animal species. Over-exploitation of natural resources through excessive hunting, fishing, and logging leads to depletion of species beyond their recovery capacity. Pollution and the introduction of invasive alien species further disturb ecosystems, resulting in the extinction or endangerment of many native species.
Q.8 Describe the structure and functions of Ecosystem. (5)
Answer: An ecosystem is a functional unit of nature consisting of living organisms (biotic components) and the non-living environment (abiotic components) interacting with each other. The biotic components include producers, consumers, and decomposers, while the abiotic components include air, water, soil, light, temperature, and nutrients. The structure of an ecosystem is based on the organization and interrelationship between these components.
The functions of an ecosystem include the flow of energy from producers to consumers through food chains and food webs, cycling of nutrients such as carbon, nitrogen, and water between biotic and abiotic components, and maintenance of ecological balance by regulating population size and environmental stability.
OR
Describe regulation of gene expression in bacteria. (5)
Answer: Regulation of gene expression in bacteria is mainly explained by the operon model, proposed through studies on the lac operon. An operon is a functional unit of DNA consisting of a regulator gene, promoter, operator, and structural genes. The regulator gene produces a repressor protein that controls the activity of the operon.
In the lac operon, when lactose is absent, the repressor binds to the operator and prevents transcription of structural genes. When lactose is present, it acts as an inducer by binding to the repressor, making it inactive. This allows RNA polymerase to bind to the promoter and transcribe the structural genes responsible for lactose metabolism. Thus, gene expression in bacteria is regulated by switching genes on or off according to environmental needs, ensuring efficient use of energy and resources.
Q.9 Describe various chromosomal disorders. (5)
Answer: Chromosomal disorders are genetic conditions caused by abnormalities in the number or structure of chromosomes. One such disorder is Down’s syndrome, which occurs due to the presence of an extra copy of chromosome 21 (trisomy 21) and is characterized by intellectual disability and distinct facial features. Turner’s syndrome is caused by the absence of one X chromosome in females (XO), leading to short stature and underdeveloped reproductive organs. Klinefelter’s syndrome occurs in males due to the presence of an extra X chromosome (XXY), resulting in sterility and development of female secondary sexual characteristics. These disorders arise due to errors during cell division such as non-disjunction.
OR
Describe Pedigree analysis. (5)
Answer: Pedigree analysis is a genetic method used to study the inheritance of traits and diseases through successive generations of a family. It involves the use of standard symbols to represent males, females, affected individuals, and carriers, making the pattern of inheritance easy to understand.
Through pedigree analysis, scientists can determine whether a trait is autosomal or sex-linked and whether it is dominant or recessive in nature. It helps in predicting the probability of occurrence of genetic disorders in future generations. Pedigree analysis is also useful in genetic counseling to advise families about the risk of inherited diseases and their management.
Note:
This question paper has been solved by subject experts of Assam Eduverse to help students understand answers clearly and score better in examinations. Our platform provides reliable Assam-specific study materials, ASSEB solutions, expert notes, and exam-oriented guidance in a simple and student-friendly manner.
Students are encouraged to visit our website for more quality learning resources and share this material with friends and classmates to help them in their exam preparation.
🎓 About Assam Eduverse
Assam Eduverse is the best educational platform in Assam, offering SEBA, AHSEC (ASSEB), SCERT, CBSE, and Assam Board Solutions along with study materials, notes, and exam preparation guides to help students learn smarter and score higher.
Our expert-prepared answers and MCQs follow the latest Assam Board Syllabus and NCERT Syllabus. We make learning simple, accessible, and effective for all students preparing for board or competitive exams.📘 Visit Assam Eduverse for free Assam Board Solutions, notes, and Study Materials prepared by experts.
