SEBA Solutions for Class 9 Advanced Geography Chapter 4 : Human Settlement | Assam Eduverse
Chapter Overview:
Assam Eduverse presents detailed and student-friendly Solutions for SEBA (ASSEB) Class 9 Advanced Geography Chapter 4 – Human Settlement. These solutions cover all intext questions and exercise questions with step-by-step explanations. Students can use these expert-curated answers to boost exam scores and understand key concepts.
This chapter explores the origin and growth of human settlements, their classification, and characteristics. It examines rural and urban settlements, including their origin, growth, and hierarchy, as well as the interrelationship between rural and urban areas. Students will gain an understanding of how human settlements develop, their patterns, and the social, economic, and environmental factors influencing them.
The following sections include intext questions, exercise questions, and MCQs with answers and explanations for easy exam preparation.
SEBA Solutions for Class 9 Advanced Geography Chapter 4 : Human Settlement Solutions | Question Answer
EXERCISE
Q1. What do you mean by ‘Human Settlement’? Discuss briefly about its origin and growth.
Answer: A human settlement is a place where people live, either permanently or temporarily. Its origin is closely tied to the development of agriculture about 12,000 years ago, which allowed humans to adopt a sedentary lifestyle instead of being nomadic. The first permanent settlements emerged near farmlands to stay close to crops and water sources.
The growth of settlements depends on favorable conditions such as availability of water, fertile soil, natural resources, security from hazards, and good transport and communication networks. River valleys and plains attracted dense populations due to agriculture, while mineral and forest resources supported economic activities. Over time, settlements expanded into towns and cities, forming the basis of human civilization and organized communities.
Q2. What is meant by ‘Settlement Geography’? Write briefly about its main subject matter.
Answer: Settlement Geography is an important branch of Human Geography. It is the study of human settlements, their origin, growth, and distribution, as well as their relationship with the physical, cultural, and socio-economic factors in the surrounding environment.
The main subject matter of settlement geography includes:
- The location, situation, and shape of settlements.
- The origin, growth, and historical changes of settlements.
- The classification of settlements (e.g., rural vs. urban).
- The spatial distribution and patterns of settlements.
- The internal structure and land use patterns of settlements.
- The interrelationship between settlements of different types.
Q3. Present the classification of human settlements with examples.
Answer: Human settlements can be classified based on occupation, form, and pattern:
Based on Occupation:
- Rural Settlement: Main occupation is agriculture, fishing, or other primary activities. Example: a farming village.
- Urban Settlement: Main occupation is manufacturing, trade, commerce, and services. Example: a town or city.
Based on Form or Shape:
- Dispersed Settlement: Houses scattered over a wide area, common in hilly regions or low-density agricultural belts. Example: mountainous settlements.
- Nucleated Settlement: Houses clustered together in a compact area, common in fertile plains.
Based on Pattern (for Nucleated Settlements):
- Rectangular/Square: Grid-like layout, e.g., Chandigarh.
- Linear: Houses along a road, railway, river, or coastline.
- Circular: Houses arranged around a central pond, lake, or temple.
- Star-like: Houses spread out from a central point, e.g., road intersection.
- Triangular: Houses at the confluence of two rivers or roads.
Q4. What do you mean by rural and urban settlement? Write the characteristic differences between these settlements.
Answer: A rural settlement is a place where the majority of people are engaged in primary economic activities like agriculture, fishing, or forestry. Whereas, an urban settlement is a place where the majority of people are engaged in non-agricultural activities such as manufacturing, trade, and services.
The characteristic differences are:
- Rural settlements are dominated by primary occupations, while urban settlements are dominated by secondary, tertiary, and quaternary occupations.
- Urban settlements typically have a larger population and higher population density than rural settlements.
- The landscape of rural settlements is more natural, consisting of agricultural fields, forests, etc. The urban landscape is largely man-made, with buildings, roads, and infrastructure.
- Urban settlements have more advanced facilities like healthcare, education, transport, and communication compared to rural settlements.
Q5. Mention the basic differences between dispersed settlement and nucleated settlement.
Answer: In a dispersed settlement, houses and buildings are scattered over a wide area with no central cluster. This type of settlement is common in regions with unfavourable physical conditions such as rugged mountains, deserts, or areas with large agricultural landholdings.
On the other hand, in a nucleated settlement, houses and buildings are closely clustered together, forming a compact and dense settlement. This pattern is typical in areas with favourable conditions like fertile plains or regions where people prefer to live together for social security and convenience.
Q6. Write in brief about the different types of settlements under the category of nucleated settlements with examples and diagrams.
Answer: The different types of nucleated settlements include:
Rectangular Settlement: Houses and roads are arranged in a grid-like pattern, intersecting at right angles. This type is common in flat, fertile plains.
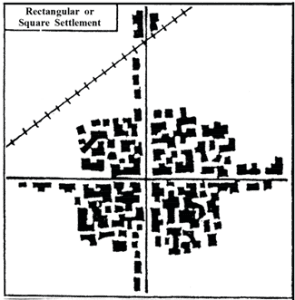
Linear Settlement: Houses are built in a line along a major transport route, river, canal, or coastline. This is often seen in river valleys or foothills of mountains.
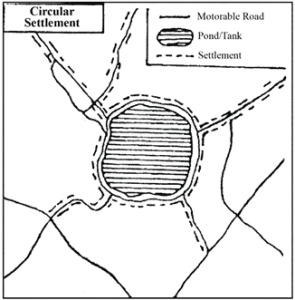
Circular Settlement: Houses are arranged in concentric circles around a central feature such as a pond or community hall.
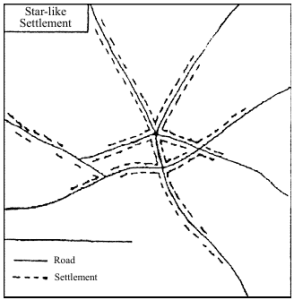
Star-like Settlement: This develops at intersections of several roads, with houses spreading outwards along each road, forming a star shape.
Triangular Settlement: Houses form a triangular pattern, often at the confluence of rivers or road junctions.
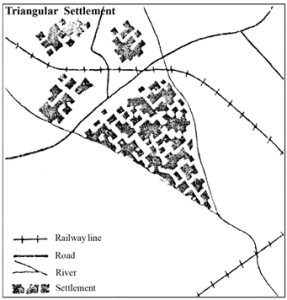
Q7. Write briefly about the origin and growth of urban settlements.
Answer: Urban settlements or towns do not originate in isolation; they often grow out of rural settlements. A village, due to its favourable location, an increase in population, and the development of non-agricultural activities, can be transformed into a town. The main factors for the origin and growth of towns are:
- Trade and Commerce: Many ancient towns were established as trade centres along old roads or rivers.
- Resource availability: The discovery of valuable minerals or other resources can lead to the growth of an industrial town.
- Administrative or defence functions: Some towns are established to serve as administrative centres for a region or as military bases.
- Transport and communication: Towns often grow at major transport hubs, such as railway junctions or seaports.
- Specialized functions: Modern towns can also grow based on specific functions like tourism, education, or healthcare.
Q8. Classify the urban settlements with examples according to functions.
Answer: Urban settlements can be classified based on their primary function.
- Administrative Towns: These towns serve as the administrative headquarters of a region or country. (e.g., Gandhinagar, Chandigarh).
- Industrial Towns: These towns have a strong focus on manufacturing and industries. (e.g., Jamshedpur, Bhilai).
- Transport Towns: These towns are major transport hubs, such as a port or a railway junction. (e.g., Haldia, Paradeep).
- Commercial Towns: These towns are centres of trade and commerce. (e.g., Kolkata, Mumbai).
- Cultural/Pilgrim Towns: These towns are important religious or cultural centres. (e.g., Varanasi, Puri).
- Educational Towns: These towns are known for their educational institutions. (e.g., Oxford, Cambridge).
- Defence Towns: These towns are important military or defence bases.
- Recreational/Tourist Towns: These towns attract tourists and are known for their natural beauty or recreational activities. (e.g., Darjeeling, Mussoorie).
Q9. What do you mean by ‘hierarchy of settlements’? Write about this with examples and diagrams.
Answer: The hierarchy of settlements classifies settlements according to their size and functions. Smaller settlements have fewer people and limited functions, while larger settlements have bigger populations and diverse functions. When arranged in order, it forms a hierarchy from the smallest to the largest.
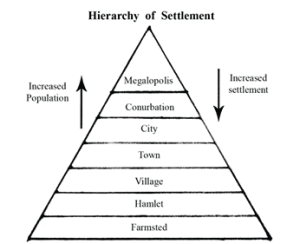
- Farmstead: A single isolated house.
- Hamlet: A small cluster of houses.
- Village: A larger rural settlement with more facilities.
- Town: A settlement dominated by non-agricultural activities with more population and functions than a village.
- City: A large urban settlement with multiple functions and complex infrastructure.
- Conurbation: Several towns or cities merged into a large urban area.
- Megalopolis: Multiple conurbations merged to form a massive, highly urbanized region.
As we move up the hierarchy, the population and functions increase, while the number of settlements decreases.
Q10. Write briefly about the landuse pattern of rural and urban settlements.
Answer: Rural Landuse: In rural settlements, land use is largely influenced by nature. The dominant use is agricultural land, supplemented by forests, pastures, and homesteads. Human activities depend heavily on the natural environment, and population density is generally low.
Urban Landuse: Urban land use is primarily man-made and diverse. The city center, or Central Business District (CBD), is dominated by commercial and financial institutions, with high-rise buildings and dense daytime population. Moving outward, land use shifts to residential areas, industrial zones, and institutional spaces. The urban fringe or suburbs exhibit a mixed land use, combining urban and rural characteristics.
Q11. What do you mean by ‘Central Business District’? Mention its basic characteristics.
Answer: The Central Business District (CBD) is the core area of a city or town, which is the main hub of commercial and financial activities. It is a very important part of the city in terms of its functions.
Basic characteristics of the CBD:
- High Land Value: Land in the CBD is limited and very expensive, which leads to the construction of high-rise buildings.
- Concentration of Businesses: It has a heavy concentration of commercial establishments, banks, corporate offices, and wholesale and retail stores.
- High Population Density: The population density during the day is very high due to a large number of people working and visiting the area.
- Dominant Land Use: The primary land use is commercial, with very little residential land use.
Q12. Write briefly about the relationship between rural and urban settlements.
Answer: Rural and urban settlements have a symbiotic relationship and are interdependent. A rural settlement cannot exist in isolation from its neighbouring town, and vice versa.
Rural to Urban: Rural settlements depend on urban settlements for various services and goods. They supply agricultural products like food grains, vegetables, fruits, and raw materials for industries to the urban areas. In return, they get access to modern education, healthcare, industrial products, and markets for their goods.
Urban to Rural: Urban settlements depend on rural areas for a constant supply of food and labour. The rural-urban relationship is facilitated by well-developed transport and communication systems.
Q13. Write short notes:
(a) Human Settlements and Settlement Geography:
Human settlements are places where people live permanently or temporarily. Settlement geography studies the location, growth, distribution, and functions of settlements, along with their interaction with the environment.
(b) Linear Settlement:
Houses are arranged in a straight line along roads, rivers, railways, or coastlines. Common in river valleys, transport routes, and foothills of mountains.
(c) Circular Settlement:
Houses are built around a central point like a pond, lake, or temple. Provides equal access to the central resource and forms a circular pattern.
(d) Star-like Settlement:
Settlement develops around the intersection of roads. Houses spread outward along the roads, forming a star-shaped pattern.
(e) Culture and Educational Town:
A town primarily developed around cultural or educational activities. It may have universities, colleges, museums, and cultural institutions attracting population and trade.
(f) Rural-Urban Continuum:
The gradual transition from rural to urban areas, where land use, population density, and lifestyle change progressively without a sharp boundary between village and city.
(g) Hierarchy of Settlements:
Hierarchy of settlements is the arrangement of settlements in a definite order based on size, population, and functions. Smaller settlements like farmsteads and hamlets are at the bottom, while larger settlements like towns, cities, and megalopolises are at the top. As you move up the hierarchy, population and services increase, but the number of settlements decreases.
(h) Urban Fringe:
The urban fringe is the zone surrounding a city where urban and rural land uses mix. It often includes suburbs, industrial areas, and new residential developments. This area represents a transition from high-density urban zones to low-density rural regions.
(i) Satellite Town:
A satellite town is a smaller town located near a major city but is independent in administration and functions. It supports the nearby city by providing residential, commercial, or industrial services and helps reduce congestion in the main city.
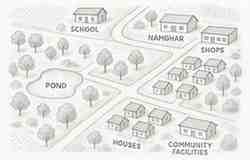
Q14. Prepare a sketch-map of your village or town show-ing the human settlements including the location of school, namghar (player hall), shop, etc under the guidance of your teacher and mention the type of settlement.
Answer:
🎓 About Assam Eduverse
This solution is prepare by Assam Eduverse – your reliable educational hub for academic content, study materials, and exam preparation for Assam Board and other state-level exams. Follow Assam Eduverse for accurate, exam-ready NCERT solutions, notes, MCQs, and free study materials.
