SEBA Solutions for Class 10 Advanced Geography Chapter 5 : Regional Geography of Japan | Assam Eduverse
Chapter Overview:
Assam Eduverse presents detailed and student-friendly Solutions for SEBA (ASSEB) Class 10 Advanced Geography Chapter 5 – Regional Geography of Japan. These solutions cover all intext questions and exercise questions with step-by-step explanations. Students can use these expert-curated answers to boost exam scores and understand key concepts.
This chapter explores the regional geography of Japan, including its physical features, climate, natural resources, population distribution, and economic activities. It also examines factors influencing settlement patterns, agriculture, and industrial development. Students will gain an understanding of the relationship between Japan’s geography and its human, economic, and environmental systems.
The following sections include intext questions, exercise questions, and MCQs with answers and explanations for easy exam preparation.
SEBA Solutions for Class 10 Advanced Geography Chapter 5 : Regional Geography of Japan Solutions | Question Answer
EXERCISE
Q1. State the geographical location of Japan.
Answer: Japan is an archipelago located off the east coast of Asia in the Pacific Ocean. It is surrounded by the Sakhalin and Kuril Islands and the Sea of Okhotsk to the north, the Taiwan and East China Sea to the south, the Pacific Ocean to the east, and the Sea of Japan, Korea Strait, and Russia Sea to the west. It extends from 24° N to 46° N latitude and from 123° E to 146° E longitude, placing it mainly in the temperate climate zone.
Q2. Give a geographical description of Japan.
Answer: Japan consists of four main islands Hokkaido, Honshu, Shikoku, and Kyushu along with thousands of smaller islands, covering about 377,765 square kilometers. Situated on the Pacific Ring of Fire, it has a complex geological structure with many active volcanoes and frequent earthquakes. The country is mostly mountainous, with only 25% of the land flat. Its temperate climate varies from north to south, with Hokkaido being colder and Honshu milder. Despite being resource-scarce, Japan has become an economic powerhouse due to its skilled workforce, advanced technology, and strong industries like electronics, automobiles, and shipbuilding.
Q3. What are the major physical divisions of Japan? Briefly describe with map the landform of each division.
Answer: Japan is primarily mountainous and can be divided into four physical regions:
- Hokkaido Region: This region includes the main island of Hokkaido. It is predominantly mountainous, but between the mountain ranges, there are extensive alluvial lowlands such as the Ishikari-Yufutoh Plain. The coastal plains provide suitable areas for development and settlement.
- North-Eastern Japan Region: Covering the northern part of Honshu, this region is characterized by numerous folds and faults. It has two parallel mountain ranges, Auo and Utsu, and the Pacific coast is separated from the Japan Sea region by deep valleys.
- Central Japan Region: Located in the central part of Honshu, this region is where the Honshu and Shichito Mariana mountain ranges meet, forming the highest mountains in Japan, including Mount Fuji. It also has extensive fertile alluvial plains, such as the Kwanto and Nobi plains.
- South-Western Japan Region: This region includes southern Honshu, Shikoku, and Kyushu. It has the longest mountain ranges, plains formed from rift valleys, and a mountainous Pacific coast. The southern part of Kyushu experiences frequent volcanic activity.

Q4. Give a brief description of the land forms of Japan.
Answer: The landforms of Japan are complex and mostly mountainous, covering about 75% of the country. Japan’s geological structure is unstable, with many active and extinct volcanoes, and the region experiences frequent earthquakes. Most mountains are newly formed folded ranges. Between these rugged mountains, narrow river valleys and coastal alluvial plains provide the main areas for human settlement and agriculture. Landforms vary from north to south: Hokkaido has more extensive plains, while Honshu features the highest mountain peaks and major fertile plains such as the Kwanto Plain.
Q5. Write briefly about population growth and distribution of Japan.
Answer: Japan’s population has grown steadily over the centuries, from about 5 million in 610 A.D. to 128 million in 2007. However, the growth rate is now very low, averaging 0.4% annually, due to declining birth and death rates linked to socio-economic development.
Population distribution is highly uneven because of Japan’s mountainous terrain. Most people live in fertile river valleys and coastal plains, while the mountainous areas, which cover around 80% of the land, remain sparsely populated. The densest population is found in industrial plains such as the Tokyo-Yokohama and Kobe-Osaka regions, with densities exceeding 10,000 persons per square kilometer. Rapid industrialization and urbanization have led to increased rural-to-urban migration, and about 79% of the population now resides in urban areas.
Q6. Mention the factors which affect the density of population of Japan.
Answer: The population density of Japan is uneven due to its physical, economic, and social conditions. While some areas are highly populated, others remain sparsely inhabited because of natural and human factors. The main factors affecting population density are:
- Physiography: Mountainous and rugged terrain makes most areas unsuitable for settlement and agriculture.
- Economic Development: Industrial regions in coastal plains and river valleys attract more people.
- Climate: Colder regions like Hokkaido have lower population density than warmer southern areas.
- Urbanization: Rapid urbanization and industrialization have led to migration from rural areas to cities, increasing urban population density.
Q7. Write about the role of agriculture in the economy of Japan.
Answer: Agriculture plays a significant role in the economy of Japan, even though only about 17% of the total land area is used for farming.
- High Productivity: Japanese agriculture is highly developed and productive due to the use of modern methods and technology, along with the sufficient application of fertilizers.
- Self-Sufficiency: It enables the country to be self-sufficient in many food crops, particularly rice.
- Support to Industry: It provides raw materials to industries.
- Pisciculture: Japan is the world’s leading producer of fish, which is a major part of its food and economic system.
- Employment: A small portion of the population (6%) is engaged in agriculture, but its contribution is vital to the country’s food security and economy.
Q8. Show the main agricultural regions of Japan on a map and describe the main characteristics of each region.
Answer: Japan has several important agricultural regions, mostly concentrated in the plains and valleys due to the mountainous terrain. The main regions include:
- Kanto Plain: Fertile alluvial soil, major crops include rice, vegetables, and fruits.
- Nobi Plain: Known for rice cultivation and horticulture.
- Kansai Region: Mixed farming with rice, vegetables, and tea cultivation.
- Kyushu Region: Warm climate suitable for rice, sugarcane, and fruit cultivation.
These regions benefit from favorable soil, climate, and irrigation systems, supporting high agricultural productivity.
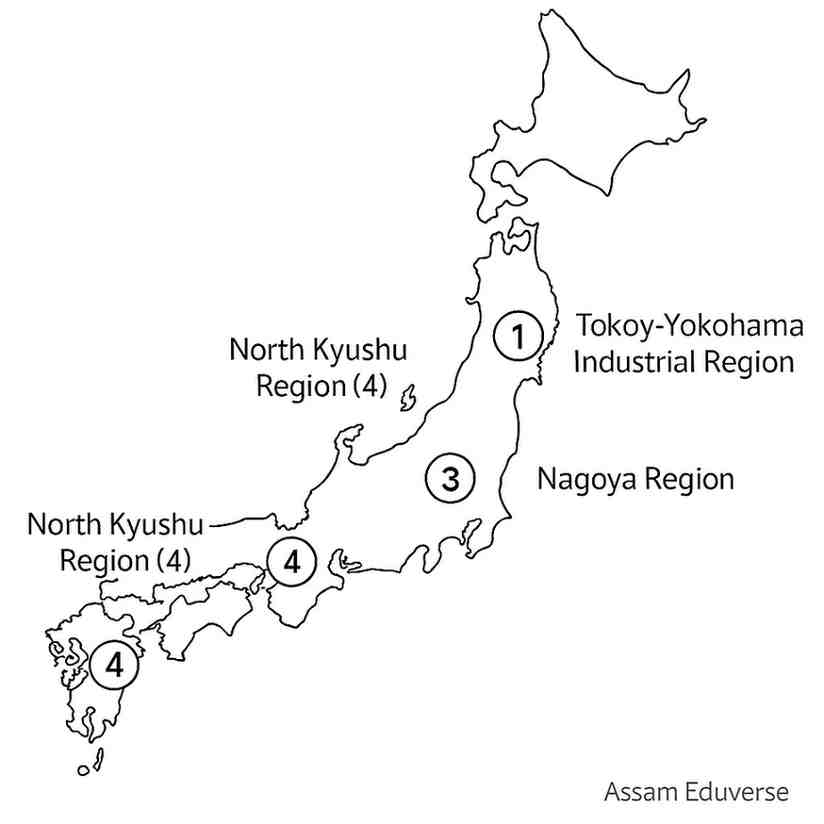
Q9. What are the chief industrial regions of Japan? Show these regions in a map and give a brief description of each region.
Answer: The major industrial regions of Japan are concentrated in coastal plains and urban centers:
- Kanto Industrial Region: Includes Tokyo-Yokohama; diversified industries such as electronics, machinery, and chemicals.
- Kansai Industrial Region: Includes Osaka-Kobe-Kyoto; known for textiles, steel, and shipbuilding.
- Chubu Industrial Region: Includes Nagoya; strong in automobile, machinery, and aerospace industries.
- Kyushu Industrial Region: Includes Fukuoka and Kitakyushu; focuses on steel, chemicals, and shipbuilding.
These regions developed due to access to ports, raw materials, labor, and transportation networks.
Q10. Write short notes on:
(a) Islands of Japan
Answer: Japan is an archipelago of more than 6,800 islands. The four main islands are Hokkaido, Honshu, Shikoku, and Kyushu. These islands are mountainous, with narrow coastal plains suitable for agriculture and settlements.
(b) Physiography of Hokkaido region
Answer: Hokkaido is the northernmost island, with volcanic mountains, plains, and basins. The Ishikari Plain is the main agricultural area, while the region experiences cold winters and heavy snowfall.
(c) Industrialisation and economic development of Japan
Answer: Japan is a highly industrialized nation with advanced technology, automobile manufacturing, electronics, shipbuilding, and chemical industries. Economic growth is supported by skilled labor, infrastructure, and exports.
(d) Terrace cultivation in Japan
Answer: Due to mountainous terrain, rice and other crops are cultivated on terraces built on slopes. This prevents soil erosion and maximizes arable land.
(e) Tokyo-Yokohama Industrial Region
Answer: It is located in the Kanto Plain, this is Japan’s largest industrial region with diverse industries including electronics, chemicals, automobiles, and shipbuilding. The region benefits from ports, transport, and a large workforce.
(f) Coastal areas of Japan:
Answer: Coastal areas are densely populated and industrialized. Ports facilitate trade and fishing, and plains along the coast support agriculture and urban settlements.
(g) Honshu island region of Japan:
Answer: Honshu is the largest island, with diverse topography including mountains, plains, and volcanic regions. Major cities, industrial centers, and fertile agricultural plains are located here.
(h) Mineral Resources of Japan:
Answer: Japan is poor in minerals and depends on imports. Limited resources include coal, petroleum, limestone, and small deposits of copper, zinc, and gold.
🎓 About Assam Eduverse
This solution is prepare by Assam Eduverse – your reliable educational hub for academic content, study materials, and exam preparation for Assam Board and other state-level exams. Follow Assam Eduverse for accurate, exam-ready NCERT solutions, notes, MCQs, and free study materials.
