NCERT Class 10 Science Chapter 4: Carbon and Its Compounds Solutions | Assam Eduverse
Chapter Overview
Assam Eduverse presents detailed and student-friendly NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 4 – Carbon and Its Compounds as per CBSE. These solutions cover all intext and exercise questions with step-by-step explanations. Students can use these expert-curated answers to boost exam scores and understand key concepts. This chapter explores the versatile nature of carbon, covalent bonding, homologous series, nomenclature of organic compounds, properties of ethanol and ethanoic acid, and important chemical reactions like combustion, oxidation, addition, and substitution.
The following sections include intext questions and exercise questions from the textbook, and multiple-choice questions (MCQs) with answers and explanations.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 4 Intext Questions
 Page 61
Page 61
Q1. What would be the electron dot structure of carbon dioxide which has the formula CO2 ?
Answer: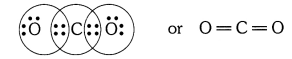
Q2. What would be electron dot structure of sulphur which is made up of eight atoms of sulphur.
Answer: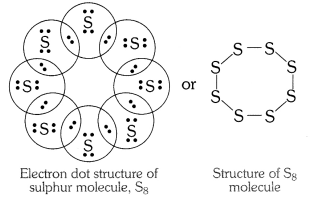
 Page 68-69
Page 68-69
Q1. How many structural isomers can you draw for pentane ?
Answer:
Three, these are n-pentane, iso-pentane and neo-pentane.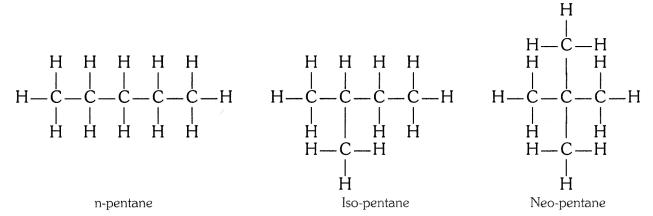
Q2. What are the two properties of carbon which lead to the huge number of carbon compounds we see around us ?
Answer:
(i) Tetravalency
(ii) Catenation.
Q3. What will be the formula and electron dot structure of cyclopentane ?
Answer:
The molecular formula of cyclopentane is C5 H10 .
The electron dot structure of cyclopentane is given on the next page.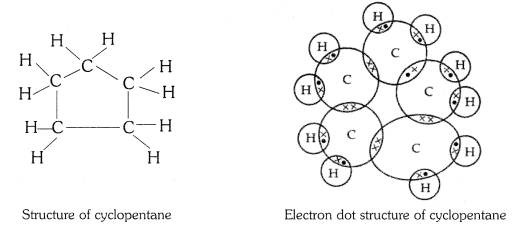
Q4. Draw the structures for the following compounds :
(i) Ethanoic acid
(ii) Bromopentane
(iii) Butanone
(iv) Hexanal
Answer:
(i) Ethanoic acid (CH3COOH)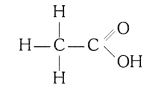
(ii) Bromopentane (C5H11Br)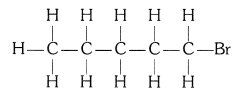
(iii) Butanone (CH3 — CH2 — COCH3)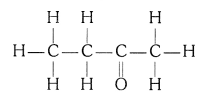
(iv) Hexanal (C5H11CHO)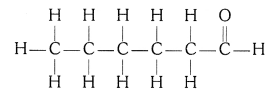
Structural isomers for bromopentane: There are three structural isomers for bromopentane depending on the position of Br at carbon 1, 2, 3.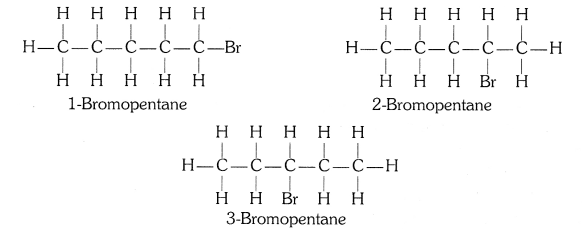
Positions 4 and 5 are same as 1, 2.
Q5. How would you name the following compounds ?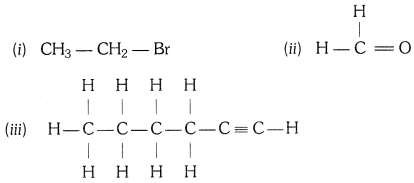
Answer:
(i) Bromoethane
(ii) Methanal
(iii) 1 – Hexyne
 Page 71
Page 71
Q1. Why is the conversion of ethanol to ethanoic acid an oxidation reaction ?
Answer:
Conversion of ethanol into ethanoic acid is an oxidation reaction because addition of oxygen to a substance is called oxidation. Here, oxygen is added to ethanol by oxidising agent like alkaline potassium permanganate or acidified potassium dichromate and it is converted into acid.
Q2. A mixture of oxygen and ethyne is burnt for welding. Can you tell why a mixture of ethyne and air is not used ?
Answer:
A mixture of ethyne and air is not used for welding because burning of ethyne in air produces a sooty flame due to incomplete combustion, which is not enough to melt metals for welding.
 Page 74
Page 74
Q1. How would you distinguish experimentally between an alcohol and a carboxylic acid ?
Answer:
Differences between alcohol and carboxylic acid
| Test | Alcohol | Carboxylic acid |
| (i) Litmus test | No change in colour. | Blue litmus solution turns red. |
| (ii) Sodium hydrogen carbonate test | C2H5OH + NaHCO3 → No reaction No brisk effervescence. | CH3COOH + NaHCO3 → CH3COONa + H2O + CO2 Brisk effervescence due to evolution of CO2. |
| (iii) Alkaline potassium permanganate | On heating, pink colour disappears. | Does not happen so. |
Q2. What are oxidising agents ?
Answer:
Oxidising agents are the substances which give oxygen to another substances or which remove hydrogen from a substance.
For example, acidic K2Cr2O7 is an oxidising agent, that converts (oxidises) ethanol into ethanoic acid.
 Page 76
Page 76
Q1. Would you be able to check if water is hard by using a detergent ?
Answer:
No, because detergents can lather well even in hard water. They do not form insoluble calcium or magnesium salts (scum). On reacting with the calcium ions and magnesium ions present in the hard water.
Q2. People use a variety of methods to wash clothes. Usually after adding the soap, they ‘beat’ the clothes on a stone, or beat it with a paddle, scrub with a brush or the mixture is agitated in a washing machine. Why is agitation necessary to get clean clothes ?
Answer:
It is necessary to agitate to get clean clothes because the soap micelles which entrap oily or greasy particles on the surface of dirty cloth have to be removed from its surface. When the cloth wetted in soap solution is agitated or beaten, the micelles containing oily or greasy dirt get removed from the surface of dirty cloth and go into water and the dirty cloth gets cleaned.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 4 Textbook Chapter End Questions
Q1. Ethane, with the molecular formula C2H6 has
(a) 6 covalent bonds
(b) 7 covalent bonds
(c) 8 covalent bonds
(d) 9 covalent bonds
Answer:
(b) 7 covalent bonds.
Q2. Butanone is a four-carbon compound with the functional group
(a) carboxylic acid
(b) aldehyde
(c) ketone
(d) alcohol
Answer:
(c) Ketone.
Q3. While cooking, if the bottom of the vessel is getting blackened on the outside, it means that
(a) the food is not cooked completely.
(b) the fuel is not burning completely.
(c) the fuel is wet.
(d) the fuel is burning completely.
Answer:
(b) The fuel is not burning completely.
Q4. Explain the nature of the covalent bond using the bond formation in CH3Cl.
Answer:
Covalent bond is formed by sharing of electrons so that the combining atoms complete their outermost shell.
In CH3Cl : C = 6, H = 1 and Cl = 17 And their electronic configuration is C – 2,4, H – 1 and Cl – 2, 8, 7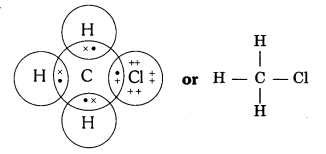
Three hydrogen atoms complete their shells by sharing three electrons (one electron each) of carbon atom.
Chlorine completes its outer shell by sharing its one out of seven electrons with one electron of carbon atom.
Thus carbon atom shares all its four electrons with three hydrogen atoms and one of chlorine atom and completes its outermost shell and single covalent bonds are formed in CH3Cl.
Q5. Draw the electron dot structures for
(a) ethanoic acid
(b) propanone
(c) H2S
(d) F2.
Answer: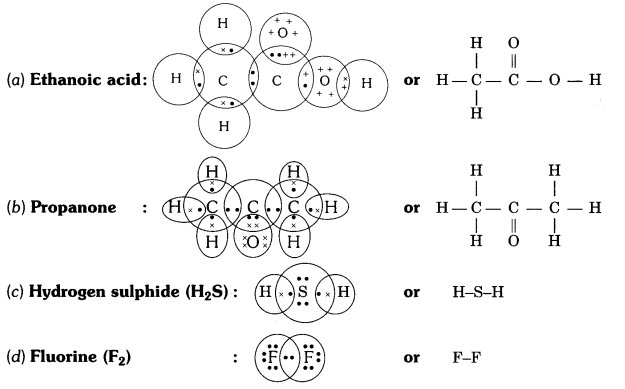
Q6. What is a homologous series ? Explain with an example.
Answer:
A homologous series is a group of organic compounds that have the same functional group and similar chemical properties. Each compound in the series differs from the next by a –CH₂– group. For example, in the alkane series, methane (CH₄), ethane (C₂H₆), and propane (C₃H₈) all follow the same pattern and show similar reactions.
Main Features of a Homologous Series:
All compounds follow the same general formula (e.g., alkanes: CₙH₂ₙ₊₂).
Each member differs from the next by –CH₂– (one carbon and two hydrogen atoms).
The molecular mass increases by 14 u for each step.
They show similar chemical properties.
Their physical properties (like boiling point) change gradually with molecular size.
| Value of n | Molecular formula | Name of compound |
| 1 | CH4 | Methane |
| 2 | C2H6 | Ethane |
| 3 | C3H8 | Propane |
| 4 | C4H10 | Butane |
| 5 | C5H12 | Pentane |
Q7. How can ethanol and ethanoic acid he differentiated on the basis of their physical and chemical properties ?
Answer:
Difference on the basis of physical properties
| Property | Ethanol | Ethanoic acid |
| (i) State | Liquid | Liquid |
| (ii) Odour | Sweet smell | Pungent vinegar-like smell |
| (iii) Melting point | 156 K | 290 K |
| (iv) Boiling point | 351 K | 391 K |
Difference on the basis of chemical properties
| Test | Ethanol | Ethanoic acid |
| (i) Litmus test | No change in the colour of litmus solution. | Blue litmus solution turns red. |
| (ii) Sodium hydrogen carbonate test | C2H5OH + NaHCO3 → No reaction No brisk effervescence. | CH3COOH + NaHCO3 → CH3COONa + H2O + CO2 Brisk effervescence due to evolution of CO2. |
| (iii) Alkaline potassium permanganate | On heating, pink colour disappears. | Does not happen so. |
Q8. Why does micelle formation take place when soap is added to water ? Will a micell be formed in other solvents such as ethanol also ?
Answer:
Micelle formation takes place when soap is added to water because the hydrocarbon chains of soap molecules are hydrophobic (water repelling) which are insoluble in water, but the ionic ends of soap molecules are hydrophilic (water attracting) and hence soluble in water.
Such micelle formation will not be possible in other solvents like ethanol in which sodium salt of fatty acids do not dissolve.
Q9. Why are carbon and its compounds used as fuels for most applications ?
Answer:
Carbon and its compounds give a large amount of heat per unit weight and are therefore, used as fuels for most applications.
Q10. Explain the formation of scum when hard water is treated with soap.
Answer:
Hard water contains salts of calcium and magnesium. Calcium and magnesium on reacting with soap form insoluble precipitate called scum. The scum formation lessens the cleansing property of soaps in hard water.
Q11. What change will you observe if you test soap with litmus paper (red and blue)?
Answer:
Red litmus will turn blue because soap is alkaline in nature. Blue litmus remains blue in soap solution.
Q12. What is hydrogenation ? What is its industrial application ?
Answer:
The addition of hydrogen to an unsaturated hydrocarbon to obtain a saturated hydro-carbon is called hydrogenation. The process of hydrogenation takes place in the presence of nickel (Ni) or palladium (Pd) metals as catalyst.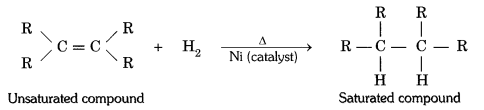
Application : The process of hydrogenation has an important industrial application. It is used to prepare vegetable ghee from vegetable oils.
Q13. Which of the following hydrocarbons undergo addition reactions :
C2H6, C3H8, C3H6, C2H2 and CH4
Answer:
Addition reactions take place only in unsaturated hydrocarbons. So addition reaction take place only in C3H6 and C2H2.
Q14. Give a test that can be used to differentiate chemically between butter and cooking oil.
To chemically differentiate between butter (a saturated fat) and cooking oil (an unsaturated fat), the Bromine water test can be used.
Test: Bromine Water Test
Procedure:
Add a few drops of bromine water to separate samples of butter and cooking oil and shake them well.Observation:
In cooking oil, the reddish-brown color of bromine water disappears due to the presence of unsaturated carbon–carbon double bonds (C=C), which react with bromine.
In butter, the reddish-brown color remains unchanged, indicating it is saturated and does not react with bromine water.
Conclusion:
Cooking oil decolorizes bromine water, while butter does not — thus, the bromine water test helps to distinguish between the two.
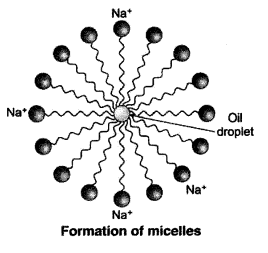
Q15. Explain the mechanism of the cleaning action of soaps.
Answer:
Soaps clean by removing oily and greasy dirt from surfaces using a process called emulsification. A soap molecule has two ends: a hydrophobic tail (repels water, attracts oil) and a hydrophilic head (attracts water). When soap is added to water and applied to an oily surface, the hydrophobic tails stick to the oil or grease, while the hydrophilic heads remain in the water. This forms tiny bubble-like structures called micelles, where the oil is trapped inside. When we rinse with water, the micelles get washed away, taking the dirt and oil along with them — leaving the surface clean.
 About Assam Eduverse
About Assam Eduverse
This solution is prepare by Assam Eduverse – your reliable educational hub for academic content, study materials, and exam preparation for Assam Board and other state-level exams. Follow Assam Eduverse for accurate, exam-ready NCERT solutions, notes, MCQs, and free study materials.

 Page 61
Page 61 About Assam Eduverse
About Assam Eduverse