AHSEC (ASSEB) Class 11 Biology Chapter 5 Solutions – Morphology of Flowering Plants | Assam Eduverse
Chapter Overview:
Assam Eduverse provides comprehensive, accurate, and student-friendly solutions for Class 11 Biology (AHSEC / ASSEB) – Unit II: Structural Organisation in Plants and Animals, Chapter 5 – Morphology of Flowering Plants. These well-structured solutions include all intext questions, exercise questions, and multiple-choice questions (MCQs) with clear explanations, helping students develop a strong conceptual understanding and prepare effectively for exams.
Chapter 5 – Morphology of Flowering Plants focuses on the external structure of angiosperms and their morphological features. Students learn about the root, stem, leaf, inflorescence, flower, fruit, and seed, along with their types, structure, and functions. The chapter also emphasizes the adaptations of different plant parts for survival in diverse habitats and introduces basic concepts of modifications in roots, stems, and leaves. Understanding these morphological traits helps students appreciate the diversity and adaptability of flowering plants.
Assam Eduverse’s Class 11 Biology Solutions are written in simple, exam-oriented, and easy-to-understand language, ensuring better clarity, quick learning, and strong academic performance. These reliable solutions help students master the morphology of flowering plants, recognize structural adaptations, and excel in AHSEC / ASSEB Biology exams with confidence and conceptual clarity.
AHSEC (ASSEB) Class 11 Biology Chapter 5 : Morphology of Flowering Plants Solutions & Question Answers
EXERCISES
Q1. How is a pinnately compound leaf different from a palmately compound leaf?
Answer: Both are compound leaves but differ in leaflet arrangement. In a pinnately compound leaf, several leaflets are arranged along a common axis called the rachis, as in neem. In a palmately compound leaf, all the leaflets are attached at a common point on the petiole tip, as in silk cotton.
Q2. Explain with suitable examples the different types of phyllotaxy.
Answer: Phyllotaxy means the arrangement of leaves on a stem or branch. It is of three types—alternate (one leaf per node, e.g. China rose, mustard), opposite (two leaves per node, e.g. guava, Calotropis), and whorled (more than two leaves per node, e.g. Alstonia).
Q3. . Define the following terms:
(a) aestivation (b) placentation (c) actinomorphic
(d) zygomorphic (e) superior ovary (f) perigynous flower
(g) epipetalous stamen
Answer:
(a) Aestivation: It is the arrangement of sepals or petals in a floral bud before it opens. The common types of aestivation are valvate, twisted, imbricate, and vexillary.
(b) Placentation: It refers to the arrangement of ovules within the ovary. The different types of placentation include marginal, axile, parietal, basal, and free central.
(c) Actinomorphic: These are flowers that can be divided into two equal halves in any plane passing through the center, showing radial symmetry.
(d) Zygomorphic: These are flowers that can be divided into two equal halves in only one vertical plane, showing bilateral symmetry.
(e) Superior ovary: An ovary that is positioned above all other floral parts such as sepals, petals, and stamens.
(f) Perigynous flower: A flower in which the floral parts are attached around the ovary at the same level, forming a cup-shaped structure called the thalamus.
(g) Epipetalous stamen: Stamens that are attached to the petals, helping in pollination. Example: brinjal.
Q4. Differentiate between
(a) Racemose and cymose inflorescence
(b) Apocarpous and syncarpous ovary
Answer:
(a) Racemose and cymose inflorescence: In racemose inflorescence, the main axis keeps growing and flowers appear laterally in acropetal order (younger near the top), as in mustard. In cymose inflorescence, the main axis ends in a flower, and growth is limited; flowers are arranged basipetally (older near the top), as in jasmine.
(b) Apocarpous and Syncarpous ovary: In an apocarpous ovary, the carpels are free from each other, as in lotus and rose. In a syncarpous ovary, the carpels are fused together, as in mustard and tomato.
Q5. Draw the labelled diagram of the following:
(i) Gram seed (dicot)
(ii) Maize seed (monocot)
Answer:
(i) Gram seed (dicot):
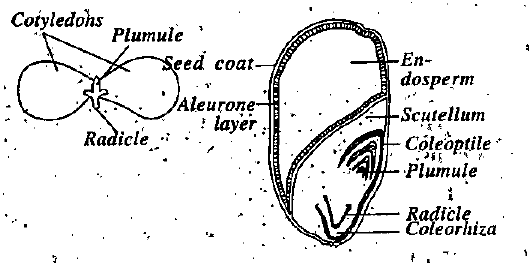
(ii) Maize seed (monocot): 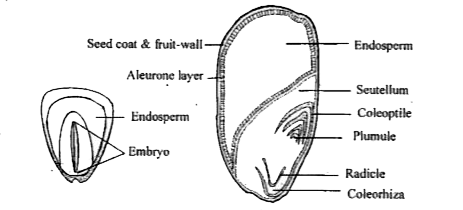
Q6. Take one flower of the family Solanaceae and write its semi-technical description. Also draw their floral diagram.
Answer: Let’s take Solanum nigrum (Black Nightshade). It is a herb with a tap root system. The stem is herbaceous and branched. Leaves are alternate and simple. The inflorescence is axillary or cymose. Flowers are bisexual and actinomorphic. Calyx and corolla each have five united parts; aestivation is valvate. Stamens are five and epipetalous. The ovary is bicarpellary, syncarpous, and superior with axile placentation. Fruit is a berry with many seeds. Floral formula: ⊕ K(5) C(5) A5 G(2).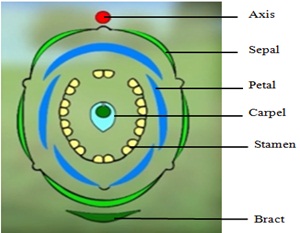
Q7. Describe the various types of placentations found in flowering plants.
Answer: The main types of placentation found in flowering plants are as follows. In marginal placentation, the ovules are arranged along the ventral suture of the ovary, as seen in pea. In axile placentation, the ovules are borne on a central axis with partitions, as in tomato. In parietal placentation, the ovules develop on the inner wall of the ovary, as in mustard. In free central placentation, the ovules are attached to a free-standing central column, as seen in primrose. In basal placentation, a single ovule is attached at the base of the ovary, as in sunflower.
Q8. What is a flower? Describe the parts of a typical angiosperm flower.
Answer: A flower is the reproductive unit of angiosperms and is considered a modified shoot that bears reproductive organs. A typical flower has four whorls: the calyx, consisting of sepals that protect the floral bud; the corolla, made up of petals that attract pollinators; the androecium, comprising stamens that produce pollen grains; and the gynoecium, which consists of carpels containing the ovary, style, and stigma, responsible for female reproduction.
Q9. Define the term inflorescence. Explain the basis for the different types of inflorescence in flowering plants.
Answer: Inflorescence refers to the arrangement and distribution of flowers on the floral axis of a plant. The classification is based on the growth pattern of the main axis. If the main axis continues to grow and produces flowers in an acropetal order (younger flowers towards the top), the inflorescence is called racemose. Whereas if the main axis terminates in a flower and further growth occurs from lateral branches in a basipetal order (younger flowers at the base), it is called cymose.
Q10. Describe the arrangement of floral members in relation to their insertion on thalamus.
Answer: There are three main types of floral arrangements based on the position of the ovary on the thalamus. In hypogynous flowers, the ovary is superior and all other floral parts such as sepals, petals, and stamens are attached below it, as in mustard. In perigynous flowers, the ovary is half-inferior, and the floral parts are attached around it at the same level, as in rose. Whereas in epigynous flowers, the ovary is inferior and the other floral parts arise from above it, as in guava.
🎓 About Assam Eduverse
Assam Eduverse is the best educational platform in Assam, offering
SEBA, AHSEC (ASSEB), SCERT, CBSE, and Assam Board Solutions along with
study materials, notes, and exam preparation guides to help students
learn smarter and score higher.
Our expert-prepared answers and MCQs follow the latest
Assam Board and NCERT syllabus. We make learning simple, accessible, and effective for
all students preparing for board or competitive exams.
📘 Visit
Assam Eduverse
for free Assam Board Solutions, notes, and study materials prepared by experts.
