AHSEC (ASSEB) Class 12 Biology Chapter 2 Solutions – Human Reproduction | Assam Eduverse
Chapter Overview:
Assam Eduverse provides comprehensive, accurate, and student-friendly solutions for Class 12 Biology (AHSEC / ASSEB) – Unit VI: Reproduction, Chapter 2 – Human Reproduction. These well-structured solutions include all intext questions, exercise questions, and multiple-choice questions (MCQs) with clear explanations, supporting a strong conceptual understanding and effective exam preparation.
Chapter 2 – Human Reproduction explores the structure and functioning of the human reproductive system. Students learn about the male and female reproductive organs, gametogenesis (spermatogenesis and oogenesis), menstrual cycle, fertilization, and implantation. The chapter also covers pregnancy, embryonic development, parturition, and lactation, highlighting the hormonal regulation of reproductive processes and the significance of reproductive health in humans.
Assam Eduverse’s Class 12 Biology Solutions are written in simple, exam-oriented, and easy-to-understand language, ensuring better clarity, quick learning, and strong academic performance. These reliable solutions help students master human reproductive processes, understand hormonal regulation, and excel in AHSEC / ASSEB Biology exams with confidence and conceptual clarity.
AHSEC (ASSEB) Class 12 Biology Chapter 2 : Human Reproduction Solutions & Question Answers
EXERCISES
Q1. Fill in the blanks:
(a) Humans reproduce _____________ (asexually/sexually)
(b) Humans are _____________ (oviparous, viviparous, ovoviviparous)
(c) Fertilisation is _____________ in humans (external/internal)
(d) Male and female gametes are _____________ (diploid/haploid)
(e) Zygote is _____________ (diploid/haploid)
(f) The process of release of ovum from a mature follicle is called
_____________
(g) Ovulation is induced by a hormone called _____________
(h) The fusion of male and female gametes is called _____________
(i) Fertilisation takes place in _____________
(j) Zygote divides to form _____________which is implanted in uterus.
(k) The structure which provides vascular connection between foetus
and uterus is called _____________
Answer:
(a) Humans reproduce sexually.
(b) Humans are viviparous.
(c) Fertilisation is internal in humans.
(d) Male and female gametes are haploid.
(e) Zygote is diploid.
(f) The process of release of ovum from a mature follicle is called ovulation.
(g) Ovulation is induced by a hormone called LH (Luteinising Hormone).
(h) The fusion of male and female gametes is called fertilisation (or syngamy).
(i) Fertilisation takes place in ampullary region of the fallopian tube.
(j) Zygote divides to form blastocyst, which is implanted in uterus.
(k) The structure which provides vascular connection between foetus and uterus is called placenta.
Q2. Draw a labelled diagram of male reproductive system.
Answer:
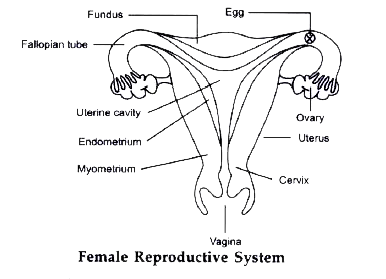
Q3. Draw a labelled diagram of female reproductive system.
Answer:
Q4. Write two major functions each of testis and ovary.
Answer: Two major functions each of testis are:
- Production of sperms (male gametes) that is spermatogenesis occurs in seminiferous tubules.
- Secretion of testicular hormones (androgens) by Leydig cells.
Two major functions each of testis are:
- Production of ovum (female gamete) that is oogenesis.
- Secretion of steroid hormones (estrogens and progesterone).
Q5. Describe the structure of a seminiferous tubule.
Answer: The seminiferous tubules are highly coiled structures in the testis where sperms are produced. They are lined with:
- Male germ cells (spermatogonia): undergo meiosis to form sperms.
- Sertoli cells: provide nutrition and help in spermiogenesis and spermiation.
The outer region (interstitial space) contains blood vessels and Leydig cells that secrete androgens.
Q6. What is spermatogenesis? Briefly describe the process of spermatogenesis.
Answer: Spermatogenesis is the process by which spermatogonia produce sperms, beginning at puberty.
- Mitosis: Spermatogonia multiply; some become primary spermatocytes.
- Meiosis I: Primary spermatocytes form two haploid secondary spermatocytes.
- Meiosis II: Secondary spermatocytes produce four spermatids.
- Spermiogenesis: Spermatids transform into motile spermatozoa.
Q7. Name the hormones involved in regulation of spermatogenesis.
Answer: The hormones involved in regulation of spermatogenesis are-
- GnRH: From hypothalamus, stimulates pituitary.
- LH: Acts on Leydig cells to secrete androgens.
- FSH: Acts on Sertoli cells to support spermiogenesis.
- Androgens: Stimulate spermatogenesis.
Q8. Define spermiogenesis and spermiation.
Answer:
- Spermiogenesis: Transformation of spermatids into motile sperms.
- Spermiation: Release of mature sperms from Sertoli cells into the lumen of seminiferous tubules.
Q9. Draw a labelled diagram of sperm.
Answer:
Q10. What are the major components of seminal plasma?
Answer: Seminal plasma (from accessory glands) contains fructose, calcium, and enzymes; bulbourethral secretions provide lubrication.
Q11. What are the major functions of male accessory ducts and glands?
Answer: The major functions of male accessory ducts and glands are-
- Accessory Ducts: Transport and store sperms; aid maturation and motility.
- Accessory Glands: Produce seminal plasma (fructose, calcium, enzymes), enhance motility, and lubricate the penis.
Q12. What is oogenesis? Give a brief account of oogenesis.
Answer: Oogenesis is the process of formation and development of a mature female gamete or ovum from the oogonia inside the ovary. It occurs in different stages as follows:
- Fetal Life: During this stage, oogonia are formed from primordial germ cells and begin meiosis I to form primary oocytes. These primary oocytes remain arrested in the prophase stage of meiosis I until puberty.
- Puberty: At puberty, some primary oocytes start growing and are surrounded by follicle cells to form primary, secondary, and later tertiary follicles.
- Completion of Meiosis I: Just before ovulation, the primary oocyte completes meiosis I, producing a secondary oocyte and a small first polar body.
- Ovulation: During ovulation, the secondary oocyte is released from the Graafian follicle into the fallopian tube.
- Completion of Meiosis II (Post-Fertilisation): Meiosis II remains incomplete until fertilisation. After fertilisation occurs, the secondary oocyte completes meiosis II to form a mature ovum and a second polar body.
Thus, oogenesis involves growth, maturation, and division stages leading to the formation of a single functional ovum from each oogonium.
Q13. Draw a labelled diagram of a section through ovary.
Answer:
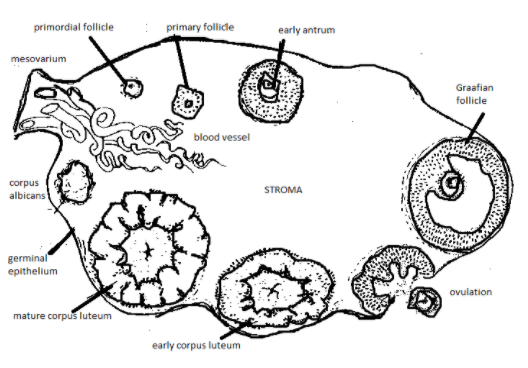
Q14. Draw a labelled diagram of a Graafian follicle.
Answer:
Q15. Name the functions of the following:
(a) Corpus luteum (b) Endometrium
(c) Acrosome (d) Sperm tail
(e) Fimbriae
Answer:
(a) Corpus luteum: It secretes progesterone, maintaining endometrium.
(b) Endometrium:It is the glandular uterine layer for implantation and pregnancy.
(c) Acrosome: It contains enzymes aiding sperm entry into ovum.
(d) Sperm tail:It provides motility using mitochondrial energy.
(e) Fimbriae: These are finger-like projections that collect the ovum post-ovulation.
Q16. Identify True/False statements. Correct each false statement to make it true.
Answer:
(a) Androgens are produced by Sertoli cells — False.
Correct: Produced by Leydig cells.
(b) Spermatozoa get nutrition from Sertoli cells — True.
(c) Leydig cells are found in ovary — False.
Correct: Found in testis.
(d) Leydig cells synthesise androgens — True.
(e) Oogenesis takes place in corpus luteum — False.
Correct: Takes place in ovary.
(f) Menstrual cycle ceases during pregnancy — True.
(g) Presence or absence of hymen is not a reliable indicator of virginity — True.
Q17. What is menstrual cycle? Which hormones regulate menstrual cycle?
Answer: The menstrual cycle is a ~28-day reproductive cycle in females.
Regulating hormones are:
- Pituitary: LH, FSH — control follicular growth and ovulation.
- Ovarian: Estrogen regenerates endometrium; progesterone maintains it.
Q18. What is parturition? Which hormones are involved in induction of parturition?
Answer: Parturition is the process of childbirth due to strong uterine contractions.
Hormones involved induction of parturition are:
- Cortisol & Estrogens: Initiate parturition signals.
- Oxytocin: Causes uterine contractions leading to foetal expulsion.
Q19. In our society the women are often blamed for giving birth to daughters. Can you explain why this is not correct?
Answer: Sex of the baby is determined by the father, not the mother.
- Female (XX): all ova carry X.
- Male (XY): sperms carry either X or Y.
If sperm with X fertilises ovum → girl (XX);
If sperm with Y fertilises ovum → boy (XY).
Q20. How many eggs are released by a human ovary in a month? How many eggs do you think would have been released if the mother gave birth to identical twins? Would your answer change if the twins born were fraternal?
Answer: One egg is released per menstrual cycle.
- Identical twins: One egg; zygote splits.
- Fraternal twins: Two eggs; each fertilised separately.
Q21. How many eggs do you think were released by the ovary of a female dog which gave birth to 6 puppies?
Answer: Six eggs were released, as dogs are polytocous (release multiple ova per cycle), each fertilised to form one puppy.
🎓 About Assam Eduverse
Assam Eduverse is the best educational platform in Assam, offering
SEBA, AHSEC (ASSEB), SCERT, CBSE, and Assam Board Solutions along with
study materials, notes, and exam preparation guides to help students
learn smarter and score higher.
Our expert-prepared answers and MCQs follow the latest
Assam Board and NCERT syllabus. We make learning simple, accessible, and effective for
all students preparing for board or competitive exams.
📘 Visit
Assam Eduverse
for free Assam Board Solutions, notes, and study materials prepared by experts.
