SEBA Solutions for Class 10 Advanced Geography Chapter 3 : Concept of Region and Regional Geography | Assam Eduverse
Chapter Overview:
Assam Eduverse presents detailed and student-friendly Solutions for SEBA (ASSEB) Class 10 Advanced Geography Chapter 3 – Concept of Region and Regional Geography. These solutions cover all intext questions and exercise questions with step-by-step explanations. Students can use these expert-curated answers to boost exam scores and understand key concepts.
This chapter explores the concept of a region and the scope of regional geography. It examines the classification and characteristics of regions, as well as the regional geography of the world, highlighting physical, cultural, economic, and political aspects. Students will gain an understanding of how regions are defined, analyzed, and compared to study human-environment interactions and global patterns.
The following sections include intext questions, exercise questions, and MCQs with answers and explanations for easy exam preparation.
SEBA Solutions for Class 10 Advanced Geography Chapter 3 : Concept of Region and Regional Geography Solutions | Question Answer
EXERCISE
Q1. What do you mean by a region? Explain the importance of region in geographical study.
Answer: A region is a part of the Earth’s surface identified by distinct geographical features, which can range from large areas like continents to small areas like villages.
Importance of a region in geographical study are :
- It helps geographers understand and analyze physical, historical, socio-economic, and political differences across the world.
- It allows comparison between regions to understand why some areas are more developed than others.
- It supports planning and development tailored to the specific environmental and social needs of each region.
Q2. Explain how a region can be identified on the earth’s surface.
Answer: A region can be identified on the Earth’s surface in two main ways:
Types of regions are :
- Homogeneous Region: Identified by uniformity in certain geographical features. For example, the Monsoon region is recognized for its similar climate, soil, and vegetation, while a linguistic region is identified by a common language spoken by its people.
- Functional Region: Defined by the functional relationship among its elements, usually centered around a main hub. Surrounding areas depend on this central place for services and activities. For example, the region around the city of Guwahati forms its functional region.
Q3. Bring out the differences between the homogeneous region and the functional region.
Answer: A homogeneous region is one that shows similarity in one or more geographical elements such as climate, soil, vegetation, or language. For example, the Equatorial Region has uniform climate, and the Hindi linguistic region is based on language similarity. The boundary of such a region is determined by the point where the common characteristic changes.
On the other hand, a functional region is based on the interdependence between a central place and its surrounding areas. The elements may not be similar but are connected through a common function like trade, transport, or administration. For example, the region around Guwahati city is a functional region, as it is linked to nearby areas through economic and transport activities.
Q4. What do you mean by regional geography of the world? What is the importance of this study?
Answer: Regional geography of the world is the study of various regions, countries, or continents to understand their geographical characteristics. It explains the physical, social, and economic conditions of a region, the inter-relationship between these elements, and the spatial variations within and across regions.
The importance of this study includes:
- It helps us to understand the physical and human environment of different parts of the world.
- It helps in identifying the socio-economic conditions of a region.
- It provides a basis for preparing development plans suited to the needs of each region.
- It helps to understand the interdependence of regions and countries for resources and economic activities.
Q5. What do you mean by ‘Natural Region’? To how many natural regions the whole earth can be divided? Write their names and show in the map.
Answer: A ‘Natural Region’ is a part of the Earth’s surface where the physical environment, including relief, climate, natural vegetation, and soil characteristics, is largely similar.
Based on climate, which is the primary influencing factor, the whole Earth can be broadly divided into 11 major natural regions.
The names of the natural regions are:
- Equatorial Region
- Monsoon Region
- Tropical Grassland Region
- Tropical Hot Desert Region
- Mediterranean Region
- Mid-Latitude Desert Region
- Mid-Latitude Temperate Region
- Mid-Latitude Grassland Region
- Cold Coniferous Forest Region
- Cold Polar Region
- High Mountain Region
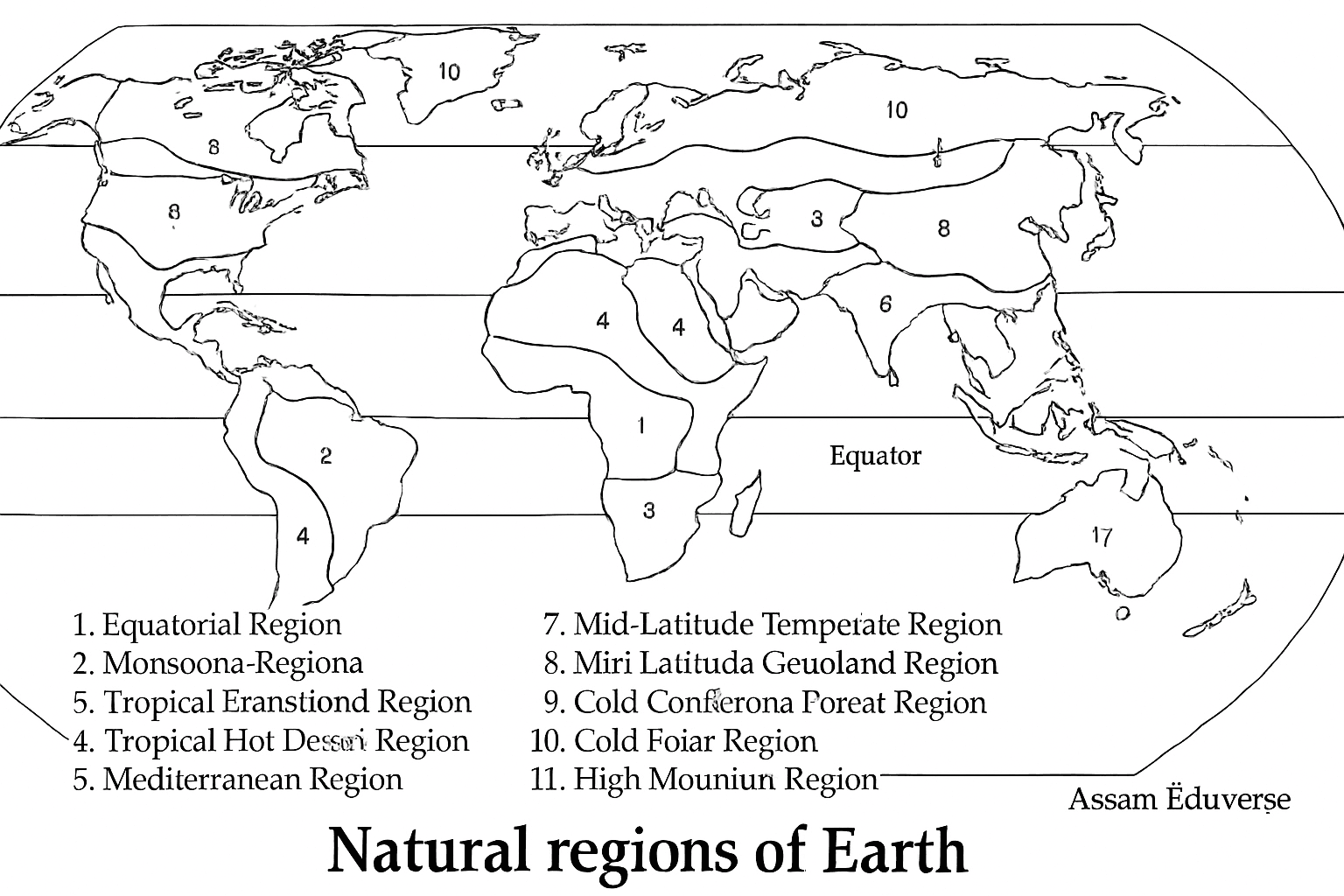
Q6. How can the regional geography of the world be understood through the study of natural regions? Write in brief.
Answer: The regional geography of the world can be understood through the study of natural regions because each region has distinct physical, environmental, and socio-economic features.
By studying natural regions, we can conclude many things such as :
- We can understand areas with similar physical characteristics such as climate, soil, and vegetation (e.g., the Equatorial region).
- We can learn how human life and economic activities are adapted to the natural environment (e.g., agriculture in Monsoon regions, nomadic lifestyle in Tundra).
- We can understand the differences in development and problems between regions, which helps in knowing the global distribution of resources.
Q7. Write about the physical environment of each of the natural regions of the world.
Answer: The physical environment of each of the natural regions of the world are:
Equatorial Region: Located near the equator. Characterized by a hot and wet climate with high temperatures (around ) and heavy rainfall (around 200 cm) throughout the year. It has dense evergreen forests, and the environment is not very suitable for human habitation due to high humidity, insects, and diseases.
Monsoon Region: Located in the tropics. Characterized by a seasonal climate with a warm and wet summer and a cold and dry winter. Average annual rainfall is around 200 cm. The natural vegetation is dominated by deciduous forests that shed their leaves in winter.
Tropical Grassland Region: Located in the interior of the continents. Has a short, warm summer and a long, dry winter. Annual rainfall is moderate (25-100 cm). The vegetation is mostly tall grasses, forming vast grasslands known as Savannah.
Tropical Hot Desert Region: Located on the western fringes of continents. The climate is hot and dry with very low rainfall (less than 20-25 cm annually). Day and night temperature differences are high. Vegetation is sparse, consisting of short grass and thorny bushes.
Mediterranean Region: Located on the western margins of continents in the mid-latitudes. Characterized by hot and dry summers and cold and wet winters, with rainfall occurring mainly in winter. The vegetation consists of evergreen short trees and shrubs.
Mid-Latitude Desert Region: Located in the central part of continents, surrounded by high mountains. It has a continental climate with a high difference between summer and winter temperatures. Rainfall is very low, and some snowfall occurs in winter. The vegetation is sparse.
Mid-Latitude Temperate Region: Found in the mid-latitudes. Summers are less intense, and winters are mild. Average annual rainfall is 75-150 cm. The vegetation is mainly deciduous, with evergreen forests in high rainfall areas and coniferous forests on hill slopes.
Mid-Latitude Grassland Region: Located in the interior of continents. Characterized by low rainfall (15-50 cm) and a high temperature difference between summer and winter. The soil is fertile due to rich organic matter. Vegetation is mainly grass, known by different local names like Prairies, Steppes, and Pampas.
Cold Coniferous Forest Region: Found in the northern hemisphere between and N latitudes. The climate is cold and dry. Summers are short, and winters are long. It is covered with evergreen coniferous forests, also known as Taiga.
Cold Polar Region: Located around the poles. Characterized by an extremely cold climate with long winters and very short summers. Rainfall is almost non-existent; instead, heavy snowfall occurs. Vegetation is limited to grass, moss, and ferns in summer.
High Mountain Region: Found in high mountain ranges like the Himalayas and the Andes. The climate and vegetation change with altitude. Temperature decreases with height, leading to different vegetation zones, from tropical forests at lower altitudes to snow and ice at the highest peaks.
Q8. Discuss about the climate and vegetation as found in different natural regions of the world.
Answer: The climate and vegetation as found in different natural regions of the world are:
- Equatorial Region: The climate is hot and wet with daily rainfall and high humidity. The vegetation is dense, tall, broadleaf evergreen forests.
- Monsoon Region: The climate is seasonal, with distinct wet and dry periods. The vegetation is primarily deciduous forests that shed their leaves during the dry winter season to conserve moisture.
- Tropical Grassland (Savannah): The climate is marked by a short rainy summer and a long, dry winter. The vegetation is characterized by tall grasses (up to 3 meters high) with scattered trees.
- Tropical Hot Desert: The climate is hot and extremely dry with very little rainfall. The vegetation is sparse and adapted to drought, consisting of thorny bushes and short grasses. Oases may support some plant life like date palms.
- Mediterranean Region: The climate has hot, dry summers and cool, wet winters. The natural vegetation is dominated by evergreen trees and shrubs with waxy leaves to withstand the dry summer heat.
- Mid-Latitude Desert: The climate is continental, with hot summers and cold winters. Rainfall is low, and the vegetation is very sparse, similar to tropical deserts.
- Mid-Latitude Temperate Region: The climate is characterized by four distinct seasons with moderate rainfall. The vegetation is mainly deciduous forests, which change colors and lose leaves in autumn and winter.
- Mid-Latitude Grassland: The climate is dry with hot summers and cold winters. The vegetation is short, nutritious grass, making it suitable for grazing.
- Cold Coniferous Forest (Taiga): The climate is cold and dry with long, severe winters and short summers. The vegetation consists of dense evergreen coniferous forests with cone-bearing trees.
- Cold Polar (Tundra): The climate is extremely cold, with the ground being permanently frozen. Vegetation is limited to mosses, lichens, and small flowering plants that grow during the short summer.
- High Mountain Region: The climate and vegetation change with altitude. As you ascend, the climate becomes colder, and the vegetation changes from tropical evergreen forests at the base to deciduous, coniferous, and finally to sparse alpine vegetation and snow cover at the highest elevations.
Q9. Give a description of the life styles of the people living in different natural regions of the world.
Answer: The people living in different natural regions of the world are :
- Equatorial Region: Due to the harsh environment of dense forests, heat, and humidity, the population is very thin. People, like the Pygmy people of the Congo basin, often live a primitive nomadic lifestyle, relying on hunting, fishing, and gathering food from the forest. Some practice shifting cultivation.
- Monsoon Region: This region has a high population density. The main occupation is agriculture. People are involved in cultivating a variety of crops like rice, wheat, and tea. The lifestyle is generally settled and agro-based.
- Tropical Grassland Region: The population is thin. People’s lifestyles are often based on animal rearing and hunting. Some parts practice small-scale cultivation of crops like jowar and cotton.
- Tropical Hot Desert Region: This region is mostly uninhabited. Nomadic pastoral groups like the Bedouins of the Sahara and Arabia make a living by rearing camels, sheep, and goats. In some oases and river valleys (like the Nile), a settled agricultural lifestyle with irrigation is possible.
- Mediterranean Region: This region is economically advanced and somewhat densely populated. The main occupation is agriculture, with people cultivating wheat, grapes, and other fruits. The lifestyle is settled, and people are also involved in industries based on fruit production, like winemaking.
- Mid-Latitude Desert Region: This region is very thinly populated. Some pastoral nomadic groups live here, but with modern advancements, some people have adopted a settled lifestyle through irrigation and mining.
- Mid-Latitude Temperate Region: This region is densely populated, and lifestyles are modern. Agriculture is done using modern, scientific techniques. People are also engaged in commercial livestock rearing and industrial activities.
- Mid-Latitude Grassland Region: Population density is thin in some parts where nomadic lifestyles based on livestock rearing dominate. However, in regions like the Prairies of North America, large-scale commercial agriculture, especially wheat cultivation, is practiced, leading to a more settled and modern lifestyle.
- Cold Coniferous Forest Region: This region is very thinly populated. The main occupations are animal hunting and wood collection. With the discovery of minerals, some areas have seen the growth of permanent settlements and economic advancement.
- Cold Polar Region: Human living is very difficult, and the population density is extremely low. The nomadic lifestyle is common, with people like the Eskimos making a living through hunting animals and fishing. They live in temporary shelters like igloos and tents. With modern influence, some have adopted a more settled lifestyle.
- High Mountain Region: This region is thinly populated due to the difficult terrain. The main occupations are livestock rearing and lumbering. A primitive form of cultivation called shifting cultivation is practiced in some valleys. Some mountainous areas have developed into popular tourist centers.
Q10. How many and what are the continents in the world? Give a brief geographical introduction of each of the continents.
Answer: There are seven continents in the world: Asia, Africa, North America, South America, Antarctica, Europe, and Oceania. A brief geographical introduction of each excluding Antarctica, which has no permanent human settlement is given below:
- Asia: The largest continent, covering about 30% of the Earth’s land area. It is located mainly in the Northern Hemisphere and is surrounded by the Northern, Pacific, and Indian Oceans. It has diverse physical features like high mountain ranges (Himalayas), plateaus (Tibetan), and fertile plains (Indo-Ganges-Brahmaputra plain). It is the most populous continent, with about 60% of the world’s population. Its economy is largely dependent on agriculture and is rich in mineral resources like petroleum.
- Africa: The second largest continent, spanning both the Northern and Southern Hemispheres. It is surrounded by the Mediterranean Sea, Indian Ocean, and Atlantic Ocean. The major part of the continent is a large plateau with scattered highlands. It is rich in water, forest, and mineral resources, and its economy is agro-based.
- Europe: The sixth largest continent, located to the north of the Mediterranean Sea. It is completely in the Northern Hemisphere and is surrounded by Asia, the Atlantic Ocean, and the Northern Ocean. Its physiography is complex, with northern plains and southern rugged highlands (Alps, Pyrenees). It has a temperate climate and is very rich in coal and iron. It is a major industrial hub of the world.
- North America: The third largest continent, located in the Northern Hemisphere. It extends from the polar region to the equatorial region and is bordered by the Northern, Pacific, and Atlantic Oceans. It has diverse physical divisions: the Rocky Mountain region, the Central Plain, and the Appalachian Highlands. It is very rich in natural resources and is highly developed in agriculture and industry.
- South America: The fourth largest continent, shaped like a reversed triangle and located south of North America. It is surrounded by the Caribbean Sea, Atlantic Ocean, and Pacific Ocean. The Andes mountain system runs along its western part. It has a diverse climate and is rich in agriculture and mineral resources.
- Oceania: The smallest continent, formed by the great island of Australia and many other islands in the south-west Pacific Ocean. It is completely in the Southern Hemisphere. Its mainland, Australia, is an ancient plateau with a large desert region. The continent has a diverse climate and is rich in mineral resources and known for sheep and cattle rearing.
Q11. Which is the largest continent in the world? Write briefly about the physiographic character of the continent.
Answer: Asia is the largest continent in the world. Asia has a very diverse physical landscape. The central part of the continent is dominated by high mountains and plateaus, such as the Himalayas, Karakoram, and Ural Mountains, along with the Tibetan and Pamir Plateaus. It is also home to the world’s highest peak, Mount Everest.
In addition, Asia has fertile plains and river deltas formed by large rivers like the Indo-Ganges-Brahmaputra, Hwang-ho, and Yangtze. The continent also includes important islands like Japan, Taiwan, the Philippines, and Sri Lanka, as well as deserts such as the Gobi, Thar, and Arabian Desert. These features make Asia’s geography extremely varied and interesting.
Q12. Which is the most populous continent in the world? Write in brief about the population and economic characteristics of that continent.
Answer: Asia is the most populous continent in the world. It is home to about 60.5% of the world’s population, but the distribution is uneven. The fertile river valleys and plains of the monsoon regions in the south, southeast, and east are very densely populated. Around 61% of Asia’s population lives in just China and India.
The economy of Asia is still largely agriculture-based, producing important crops like rice, wheat, sugarcane, and tea. The continent is also rich in natural resources such as petroleum, coal, iron ore, and natural gas. With rapid industrialization in countries like Japan, China, and South Korea, Asia has become a major economic power in the world.
Q13. Mention the geographical characteristics of the continent of Europe.
Answer: Europe is located along the north-eastern boundary of Asia and lies completely in the Northern Hemisphere. It is the sixth largest continent. The physiography of Europe is diverse: the northern part, from France to the Ural Mountains, is mostly plain land, while the southern part is rugged with mountains and plateaus like the Alps and Caucasus. The highest peak is Mount Elbrus, and the continent is rich in rivers and lakes, including the Danube, Volga, Rhine, and Ladoga Lake.
Europe has a mostly temperate climate, with coastal areas influenced by the ocean for an equitable climate, while the northern regions experience a polar climate with long snowy winters. The continent is rich in mineral resources like coal and iron and is known for well-developed agriculture. Being the birthplace of the Industrial Revolution, most European countries are highly industrialized and economically advanced.
Q14. Write briefly about the topography and mineral resources of the continent of North America.
Answer: North America has a very diverse topography that can be divided into four main regions. The Rocky Mountain or Cordillera Region in the west includes the Rocky Mountains, Sierra Nevada, Cascade ranges, and plateaus like the Great Basin. The Great Plain Region lies between the Rockies and the Appalachian Highlands and is a vast, fertile plain formed by the Mississippi-Missouri river system. The Appalachian Highland Region in the east consists of old, low hills, mountains, and plateaus, while narrow coastal plains are found along the Atlantic and Pacific coasts.
North America is very rich in mineral resources. It produces large quantities of coal, petroleum, and natural gas in Canada, the USA, and Mexico. The continent also has important deposits of iron, nickel, cobalt, and copper. Additionally, the many rivers and lakes make North America a major producer of hydro-power, supporting both industry and agriculture.
Q15. Write in brief about the drainage and vegetation of the continent of South America.
Answer: South America has an extensive and diverse drainage system. The western part is dominated by the Andes Mountains, while the rest of the continent consists of plains formed by major rivers and their tributaries. The main rivers include the Amazon, Orinoco, Parana, Paraguay, and Uruguay. The continent is also home to the world’s highest lake, Titicaca.
The continent’s vegetation is equally diverse. About 40% of South America is covered with dense equatorial and tropical forests, especially in the Amazon basin. Grasslands, called Llanos in the Orinoco basin and Pampas in the Paraguay-Parana-Uruguay basin, are common. Dry regions like the Atacama and Patagonia deserts have sparse desert vegetation due to low rainfall.
Q16. Mention the major mountain systems and rivers of the world and show them in the map.
Answer: The world has several major mountain systems. The Andes in South America are the longest, while the Himalayas in Asia are the highest. North America has the Rockies, and Europe has the Alps. The Great Dividing Range is found in Australia, and the Ural Mountains in Russia mark the boundary between Europe and Asia.
The world’s major rivers include the Nile in Africa, the Amazon in South America, and the Congo in Africa. North America has the Mississippi-Missouri system, Asia has the Ganges-Brahmaputra and Yangtze, Europe has the Volga, and Australia has the Murray-Darling river system. These rivers and mountain systems are important for climate, agriculture, and human settlements.
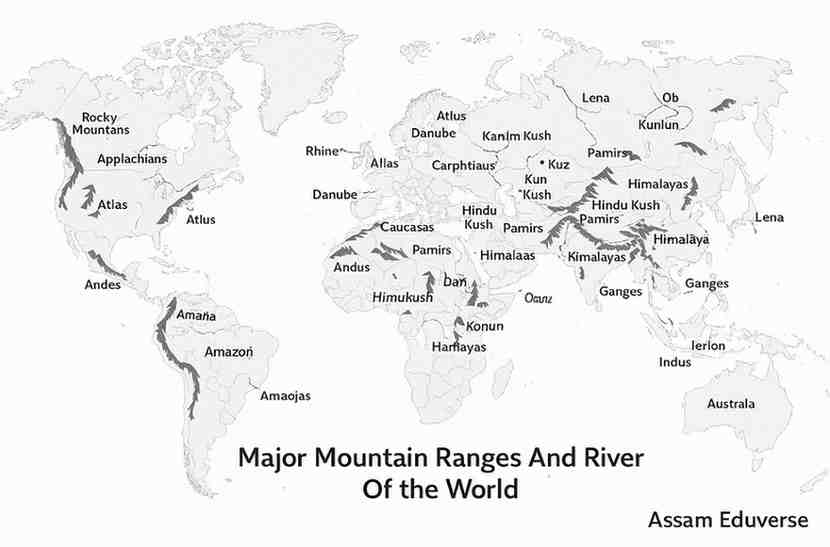
Q17. Write in brief about the climate and mode of living in the continent of Africa.
Answer: A large part of Africa lies in the tropical climate zone. The equatorial region experiences a hot and wet climate, while the northern and southern margins have sub-tropical and temperate climates. Desert regions like the Sahara and Kalahari are hot and dry with very little rainfall. Rainfall is high in equatorial and coastal areas but extremely low in the deserts.
The mode of living in Africa varies according to the region. In desert areas, people often follow a nomadic lifestyle, raising animals like camels, sheep, and goats. About 70% of the population depends on agriculture, using fertile river valleys and grasslands for cultivation. With the growth of cities, the number of people following an urban lifestyle is increasing, and they are engaged in modern economic activities.
Q18. Which is the smallest continent in the world? Write briefly about the geographical situation of that continent.
Answer: Oceania is the smallest continent in the world. It is located in the southern and western hemispheres and consists of the main island of Australia along with many other islands in the south-west Pacific Ocean, including New Zealand and New Guinea. The total land area is about 9 million sq. km, making it the smallest continent.
The mainland of Australia is an ancient plateau with a large desert in the central part, while the eastern region has a highland area called the Great Dividing Range. The continent has relatively few rivers, with the Murray and Darling being the largest. Oceania also includes thousands of islands, broadly grouped into Micronesia, Melanesia, and Polynesia.
Q19. Write short notes:
(a) Major Grassland Regions of the World
Answer: The major grassland regions of the world are divided into tropical grasslands and mid-latitude grasslands. Tropical grasslands (Savannah) are found in the tropical zone with a short wet summer and long dry winter, such as the Llanos of Venezuela, Campos of Brazil, and grasslands of Africa. Mid-latitude grasslands are located in the interiors of continents with low rainfall. They are called Prairies in North America, Steppes in Asia and Europe, Pampas in Argentina, Veld in South Africa, and Downs in Australia.
(b) Equatorial Natural Region
Answer: The Equatorial region lies on either side of the equator. It has a hot and wet climate, with average annual rainfall around 200 cm. The region is covered by dense evergreen forests, making it less suitable for human habitation. The population is thin, and people often follow a nomadic lifestyle based on hunting and gathering. Examples include the Amazon and Congo river basins.
(c) Mediterranean Natural Region
Answer: The Mediterranean region is found along the western margins of continents, especially around the Mediterranean Sea. It has hot, dry summers and cold, wet winters. Vegetation includes evergreen trees and shrubs with thick leaves. The region is economically advanced, with dense population and agriculture focused on fruits and winemaking.
(d) Monsoon Region
Answer: The Monsoon region experiences seasonal climate with warm, wet summers and cold, dry winters. Annual rainfall is about 200 cm, and the vegetation is mainly deciduous forests. The region is densely populated and agriculturally rich, growing crops like rice, wheat, and sugarcane. Examples include South Asia, Southeast Asia, and parts of East Africa.
(e) Topography and Climate of Asia
Answer: Asia has a diverse topography with high mountains such as the Himalayas and Karakoram, plateaus like the Tibetan and Pamir, fertile plains including the Ganges, Yangtze, and Mekong, islands such as Japan and the Philippines, and deserts like the Gobi and Thar. The continent experiences a wide range of climates: equatorial in the south, monsoon in the east and south, tropical desert in the west, temperate in the middle latitudes, and polar in the far north.
(f) Tundra Region
Answer: The Tundra region is found around the North Pole, north of the Arctic Circle. It has an extremely cold climate with long winters and short summers. The ground is often permanently frozen, and vegetation is sparse, consisting of mosses and lichens. The population is very low, and people like the Eskimos lead a nomadic lifestyle based on hunting and fishing.
(g) World Population and Its Distribution
Answer: The world’s population exceeds 7 billion, with Asia being the most populous continent. Population distribution is uneven. Fertile river valleys, coastal plains, and industrial regions are densely populated, while deserts, high mountains, and polar regions have very low population. This uneven distribution depends on climate, resources, and economic development.
(h) Tropical Grassland Region
Answer: The Tropical Grassland region is located in the interior of continents within the tropical zone. It has a short, warm wet summer and long, dry winter, with rainfall of 25–100 cm. Vegetation consists of tall grasses forming savannahs. People mostly practice livestock rearing and hunting.
(i) Tropical Hot Desert Region
Answer: The Tropical Hot Desert region lies near the Tropics of Cancer and Capricorn. It has a hot, extremely dry climate with less than 20–25 cm rainfall and large day-night temperature variations. Vegetation is sparse, with xerophytic plants having thorns and small leaves. Human habitation is low, with most people practicing nomadic pastoralism.
(j) Cold Coniferous Forest Region (Taiga)
Answer: The Cold Coniferous Forest or Taiga is in the northern hemisphere between about 50°–70° N latitude. It has a cold, dry climate with long winters and short summers. Vegetation is mainly evergreen coniferous trees (softwoods) forming dense forests. The region is thinly populated and unsuitable for agriculture. Main economic activities include lumbering and animal hunting.
🎓 About Assam Eduverse
This solution is prepare by Assam Eduverse – your reliable educational hub for academic content, study materials, and exam preparation for Assam Board and other state-level exams. Follow Assam Eduverse for accurate, exam-ready NCERT solutions, notes, MCQs, and free study materials.
