Class 9 SEBA Science Chapter 6 Solutions – Tissues (2026–27) | Assam Eduverse
Chapter Overview:
SEBA Class 9 Science Chapter 6 Tissues solutions are prepared by Assam Eduverse strictly according to the latest SEBA / ASSEB syllabus 2026–27. These SEBA Class 9 Science Chapter 6 Tissues solutions are created specifically for students searching for SEBA Class 9 Science Chapter 6 Tissues solutions that are accurate, updated, and exam-oriented. This page provides complete SEBA Class 9 Science Chapter 6 Tissues solutions, making it a reliable and trusted source for SEBA Class 9 Science Chapter 6 Tissues solutions based entirely on the official SEBA Class 9 Science textbook.
The SEBA Class 9 Science Chapter 6 Tissues solutions explain every concept included in SEBA Class 9 Science Chapter 6 Tissues solutions, such as meaning of tissues, plant tissues, meristematic tissues, permanent tissues, simple tissues, complex tissues, animal tissues, epithelial tissue, connective tissue, muscular tissue, and nervous tissue. These SEBA Class 9 Science Chapter 6 Tissues solutions help students understand theory, definitions, diagrams, and reasoning questions using SEBA Class 9 Science Chapter 6 Tissues solutions written in simple, clear, and exam-friendly language. Every SEBA Class 9 Science Chapter 6 Tissues solution strictly follows the official ASSEB Class 9 Science Chapter 6 solutions format and marking scheme.
With the complete SEBA Class 9 Science Chapter 6 Tissues solutions (2026–27), students can confidently prepare SEBA Class 9 Science Chapter 6 Tissues solutions for intext questions as well as SEBA Class 9 Science Chapter 6 Tissues solutions for chapter-end textbook exercise questions. These SEBA Class 9 Science Chapter 6 Tissues solutions include important Tissues question answers, plant and animal tissues notes, and exam-focused explanations. Assam Eduverse ensures every SEBA Class 9 Science Chapter 6 Tissues solution is syllabus-based, conceptually accurate, and fully exam-focused for SEBA and ASSEB examinations.
SEBA / ASSEB Class 9 Science Chapter 6 – Tissues Intext Questions & Answers (Latest Syllabus 2026–27)
📝Page 69
Q1. What is a tissue?
Answer:
A tissue is a group of cells that are similar in structure and/or work together to achieve a particular function.
Q2. What is the utility of tissues in multi-cellular organisms?
Answer:
Tissues provide structural and functional organization by allowing groups of similar cells to perform specific functions efficiently. This division of labour increases the efficiency and survival of multicellular organisms.
📝Page 73
Q1. Name types of simple tissues.
Answer:
The types of simple tissues are parenchyma, collenchyma, and sclerenchyma.
Q2. Where is apical meristem found?
Answer:
Apical meristem is found at the tips of roots and shoots in plants.
Q3. Which tissue makes up the husk of coconut?
Answer:
Sclerenchyma tissue makes up the husk of coconut.
Q4. What are the constituents of phloem?
Answer:
Phloem consists of sieve tubes, sieve cells, companion cells, phloem fibres, and phloem parenchyma.
📝Page 77
Q1. Name the tissue responsible for movement in our body.
Answer:
Muscular tissue is responsible for movement in our body.
Q2. What does a neuron look like?
Answer:
A neuron has a cell body with a nucleus and cytoplasm, from which extend a single long process called the axon and several short, branched processes called dendrites.
Q3. Give three features of cardiac muscles.
Answer:
Cardiac muscles are cylindrical and branched, involuntary in action, and have a single nucleus per cell.
Q4. What are the functions of areolar tissue?
Answer:
Areolar tissue fills the space inside organs, supports internal organs, connects different tissues, and helps in tissue repair.
SEBA Class 9 Science Chapter 6 – Tissues Textbook Exercise Questions & Solutions | 2026–27
Q1. Define the term “tissue”.
Answer:
A tissue is a group of similar cells that work together to perform a particular function.
Q2. How many types of elements together make up the xylem tissue? Name them.
Answer:
Xylem is made up of four types of elements: tracheids, vessels, xylem parenchyma, and xylem fibres.
Q3. How are simple tissues different from complex tissues in plants?
Answer:
Simple tissues are made up of only one type of cell that looks similar and performs a common function. Complex tissues are made up of more than one type of cell that work together to perform a specific function.
Q4. Differentiate between parenchyma, collenchyma and sclerenchyma on the basis of their cell wall.
Answer:
- Parenchyma – Has thin cell walls made of cellulose.
- Collenchyma – Has unevenly thickened cell walls at the corners, made of cellulose and pectin.
- Sclerenchyma – Has thick cell walls with lignin, making them hard and rigid.
Q5. What are the functions of the stomata?
Answer:
Stomata allow exchange of gases (oxygen and carbon dioxide) with the atmosphere and also help in the process of transpiration, i.e., the loss of water vapour from the plant.
Q6. Diagrammatically show the difference between the three types of muscle fibres.
Answer: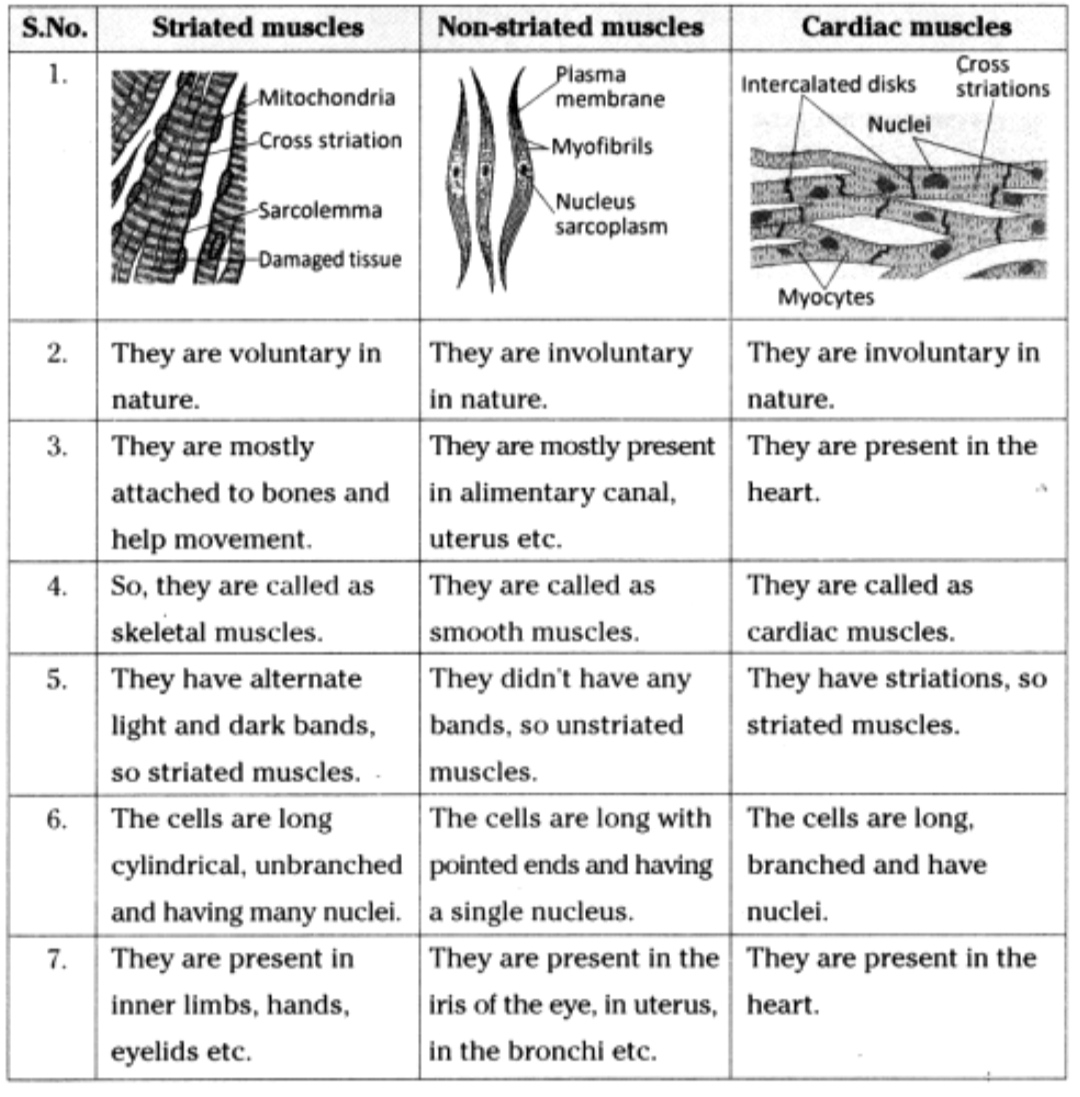
Q7. What is the specific function of the cardiac muscle?
Answer:
The specific function of the cardiac muscle is to contract and relax rhythmically and continuously to pump blood throughout the body.
Q8. Differentiate between striated, unstriated, and cardiac muscles on the basis of their structure and location in the body.
Answer:
1. Striated Muscles
- Structure: Long, cylindrical, multinucleated fibres with clear light and dark striations.
- Location: Found in muscles attached to bones (e.g., arms, legs).
2. Unstriated Muscles
- Structure: Spindle-shaped fibres, single nucleus, no striations.
- Location: Found in the walls of internal organs such as the stomach, intestines, and blood vessels.
3. Cardiac Muscles
- Structure: Branched fibres, single nucleus, faint striations, and intercalated discs.
- Location: Found only in the walls of the heart.
Q9. Draw a labelled diagram of a neuron.
Answer:
Q10. Name the following.
(a) Tissue that forms the inner lining of our mouth.
Answer: Epithelial tissue
(b) Tissue that connects muscle to bone in humans.
Answer: Tendon
(c) Tissue that stores fat in our body.
Answer: Adipose tissue
(d) Tissue that transports food in plants.
Answer: Phloem
(e) Connective tissue with a fluid matrix.
Answer: Blood
(f) Tissue present in the brain.
Answer: Nervous tissue
Q11. Identify the type of tissue in the following: skin, bark of tree, bone, lining of kidney tubule, vascular bundle.
Answer:
Skin – Epithelial tissue
Bark of tree – Protective tissue (Cork)
Bone – Connective tissue
Lining of kidney tubule – Epithelial tissue (Cuboidal)
Vascular bundle – Complex tissue (Xylem and Phloem)
Q12. Name the regions in which parenchyma tissue is present.
Answer:
Parenchyma tissue is present in the cortex and pith of stems and roots, mesophyll of leaves, and in the flesh of fruits.
Q13. What is the role of epidermis in plants?
Answer:
Epidermis protects the plant from water loss, mechanical injury, and invasion by parasites. It also helps in gas exchange and forms a continuous outer layer.
Q14. How does the cork act as a protective tissue?
Answer:
Cork cells are dead, closely packed, and their walls contain suberin, making them waterproof and impervious to gases. Cork thus protects the plant from infection and water loss.
Q15. Complete the following chart:
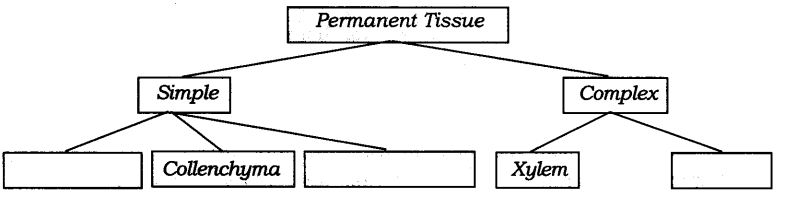
Answer: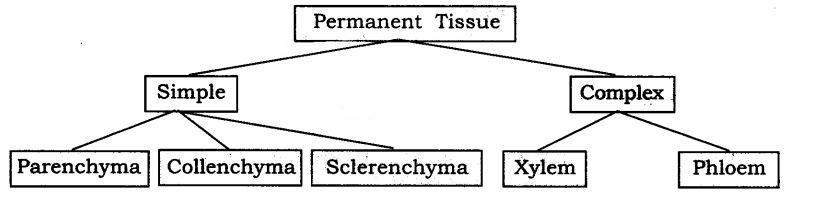
🎓 About Assam Eduverse
Assam Eduverse is the best educational platform in Assam, offering SEBA, AHSEC (ASSEB), SCERT, CBSE, and Assam Board Solutions along with study materials, notes, and exam preparation guides to help students learn smarter and score higher.
Our expert-prepared answers and MCQs follow the latest Assam Board Syllabus and NCERT Syllabus. We make learning simple, accessible, and effective for all students preparing for board or competitive exams.📘 Visit Assam Eduverse for free Assam Board Solutions, notes, and Study Materials prepared by experts.
