NCERT Class 10 Science Chapter 13: Magnetic Effects of Electric Current Solutions | Assam Eduverse
Chapter Overview
Assam Eduverse presents detailed and student-friendly NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 13 – Magnetic Effects of Electric Current as per CBSE Cirriculum. These solutions cover all intext and exercise questions with step-by-step explanations. Students can use these expert-curated answers to boost exam scores and understand key concepts.This chapter explores magnetism produced by electric current, magnetic field lines, right-hand thumb rule, Fleming’s left hand rule, Fleming’s right hand rule. It also highlights the importance of domestic electric circuits and safety devices.
The following sections include intext questions, exercise questions from the textbook, and multiple-choice questions (MCQs) with answers and explanations.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 13 Intext Questions
📝PAGE 196
Q1. Why does a compass needle get deflected when brought near a bar magnet?
Answer: A compass needle gets deflected when brought near a bar magnet because the magnet creates a magnetic field around it. The needle, which itself is a small magnet, experiences a force due to this magnetic field and aligns itself along the direction of the magnetic lines of force.
📝PAGE 200
Q1. Draw magnetic field lines around a bar magnet.
Answer:
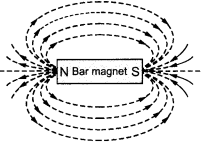
Q2. List the properties of magnetic lines of force.
Answer:
- They originate from the north pole and end at the south pole.
- They form closed loops.
- They never intersect each other.
- The closer the lines, the stronger the magnetic field.
Q3. Why don’t two magnetic lines of force intersect each other?
Answer: Two magnetic field lines never intersect because at the point of intersection, there would be two directions of the magnetic field, which is not possible.
📝 PAGE 201-202
Q1. Consider a circular loop of wire lying in the plane of the table. Let the current pass through the loop clockwise. Apply the right-hand rule to find out the direction of the magnetic field inside and outside the loop.
Answer: Using the right-hand rule, curl your fingers in the direction of current; your thumb points in the direction of the magnetic field. Inside the loop, the magnetic field is directed downward, and outside the loop, it is directed upward.
Q2. The magnetic field in a given region is uniform. Draw a diagram to represent it.
Answer:
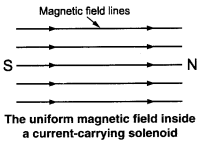
Q3. Choose the correct option.
The magnetic field inside a long straight solenoid carrying current: (a) is zero.
(b) decreases as we move towards its end.
(c) increases as we move towards its end.
(d) is the same at all points.
Answer: (d) is the same at all points.
📝PAGE 203-204
Q1. Which of the following property of a proton can change while it moves freely in a magnetic field? (There may be more than one correct answer.) (a) mass
(b) speed
(c) velocity
(d) momentum
Answer: (c) velocity, (d) momentum
Q2. In Activity 13.7, how do we think the displacement of rod AB will be affected if:
(i) current in rod AB is increased
(ii) a stronger horse-shoe magnet is used
(iii) length of the rod AB is increased
Answer: In all three cases, the force on the rod will increase, hence displacement will be more.
Q3. A positively-charged particle (alpha-particle) projected towards west is deflected towards north by a magnetic field. The direction of magnetic field is: (a) towards south
(b) towards east
(c) downward
(d) upward
Answer: (d) upward
📝PAGE 238
Q1. Name two safety measures commonly used in electric circuits and appliances.
Answer:
- Electric fuse
- Earth wire
Q2. An electric oven of 2 kW power rating is operated in a domestic electric circuit (220 V) that has a current rating of 5 A. What result do you expect? Explain.
Answer: Current drawn = Power / Voltage = 2000 / 220 ≈ 9.09 A, which is more than 5 A. Hence, the fuse will blow and the circuit will break due to overloading.
Q3. What precaution should be taken to avoid the overloading of domestic electric circuits?
Answer:
To avoid the overloading of domestic electric circuits, the following precautions should be taken :
- The wires used in the circuit must be coated with good insulating materials like PVC, etc.
- The circuit must be divided into different sections and a safety fuse must be used in each section.
- High power appliances like air-conditioner, refrigerator, a water heater, etc. should not be used simultaneously.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 13 Textbook Chapter End Questions
Q1. Which of the following correctly describes the magnetic field near a long straight wire?
(a) The field consists of straight lines perpendicular to the wire.
(b) The field consists of straight lines parallel to the wire.
(c) The field consists of radial lines originating from the wire.
(d) The field consists of concentric circles centred on the wire.
Answer: (d)
Q2. At the time of short circuit, the current in the circuit:
(a) reduces substantially.
(b) does not change.
(c) increases heavily.
(d) vary continuously.
Answer: (c)
Q3. State whether the following statements are true or false.
(a) The field at the centre of a long circular coil carrying current will be parallel straight lines. True
(b) A wire with a green insulation is usually the live wire of an electric supply. False
Q4. List two methods of producing magnetic fields.
Answer:
Using a current-carrying straight conductor
Using a solenoid
Q5. When is the force experienced by a current–carrying conductor placed in a magnetic field largest?
Answer: When the conductor is placed perpendicular to the magnetic field.
Q6. Imagine that you are sitting in a chamber with your back to one wall. An electron beam, moving horizontally from back wall towards the front wall, is deflected by a strong magnetic field to your right side. What is the direction of magnetic field?
Answer: Using Fleming’s Left-Hand Rule, the magnetic field is directed downward.
Q7. State the rule to determine the direction of:
(i) Magnetic field around a straight conductor – Right-hand thumb rule: If the current carrying conductor is held in the right hand such that the thumb points in the direction of the current, then the direction of the curl of the fingers will give the direction of the magnetic field.
(ii) Force on a conductor in magnetic field – Fleming’s left-hand rule : Current Stretch the forefinger, the central finger and the thumb of the left hand mutually perpendicular to each other. If the forefinger points in the direction of the magnetic field, the middle finger in the direction of current, then the thumb points in the direction of force in the conductor.
(iii) Induced current – Fleming’s right-hand rule : Stretch the thumb, forefinger and the central finger of the right hand mutually perpendicular to each other. If the forefinger points in the direction of magnetic field, thumb in the direction of motion of the conductor, then the middle finger points in the direction of current induced in the conductor.
Q8. When does an electric short circuit occur?
Answer: When the live wire touches the neutral wire directly, allowing a large current to flow.
Q9. What is the function of an earth wire? Why is it necessary to earth metallic appliances?
Answer: Earth wire protects from electric shock by transferring excess charge to the ground. Earthing ensures user safety in case of insulation failure
It is necessary to earth metallic appliances because it ensures that if there is any current leakage in the metallic cover, the potential of the appliance becomes equal to that of the earth. The potential of the earth is zero. As a result, the person handling the appliance will not get an electric shock.
🎓 About Assam Eduverse
This solution is prepare by Assam Eduverse – your reliable educational hub for academic content, study materials, and exam preparation for Assam Board and other state-level exams. Follow Assam Eduverse for accurate, exam-ready NCERT solutions, notes, MCQs, and free study materials.
