Class 10 SEBA Science Chapter 13 Solutions – Magnetic Effects of Electric Current (2026–27) | Assam Eduverse
Chapter Overview
SEBA Class 10 Science Chapter 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric Current solutions are prepared by Assam Eduverse strictly according to the latest SEBA / ASSEB syllabus 2026–27. These SEBA Class 10 Science Chapter 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric Current solutions are created for students searching specifically for SEBA Class 10 Science Chapter 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric Current solutions that are accurate, updated, and exam-oriented. This page provides complete SEBA Class 10 Science Chapter 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric Current solutions, making it a trusted source for SEBA Class 10 Science Chapter 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric Current solutions based on the official SEBA Class 10 Science textbook.
The SEBA Class 10 Science Chapter 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric Current solutions explain all concepts included in SEBA Class 10 Science Chapter 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric Current solutions, such as magnetic field and field lines, Oersted’s experiment, Fleming’s left-hand rule, Fleming’s right-hand rule, electromagnetic induction, electric motor, and electric generator. These SEBA Class 10 Science Chapter 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric Current solutions help students understand diagrams, numericals, and theory using SEBA Class 10 Science Chapter 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric Current solutions written in simple and exam-friendly language, following the ASSEB Class 10 Science Chapter 13 solutions format.
With the complete SEBA Class 10 Science Chapter 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric Current solutions (2026–27), students can prepare SEBA Class 10 Science Chapter 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric Current solutions for intext questions and SEBA Class 10 Science Chapter 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric Current solutions for chapter-end textbook exercise questions. These SEBA Class 10 Science Chapter 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric Current solutions include important numericals, diagram-based questions, and exam-focused explanations. Assam Eduverse ensures every SEBA Class 10 Science Chapter 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric Current solution is syllabus-based and exam-focused.
SEBA / ASSEB Class 10 Science Chapter 13 – Magnetic Effects of Electric Current Intext Questions & Answers (Latest Syllabus 2026–27)
📝PAGE 224
Q1. Why does a compass needle get deflected when brought near a bar magnet?
Answer: A compass needle gets deflected when brought near a bar magnet because the magnet creates a magnetic field around it. The needle, which itself is a small magnet, experiences a force due to this magnetic field and aligns itself along the direction of the magnetic lines of force.
📝PAGE 228
Q1. Draw magnetic field lines around a bar magnet.
Answer:
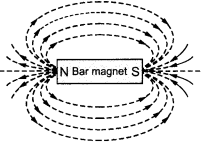
Q2. List the properties of magnetic lines of force.
Answer:
They originate from the north pole and end at the south pole.
They form closed loops.
They never intersect each other.
The closer the lines, the stronger the magnetic field.
Q3. Why don’t two magnetic lines of force intersect each other?
Answer: Two magnetic field lines never intersect because at the point of intersection, there would be two directions of the magnetic field, which is not possible.
📝 PAGE 229-230
Q1. Consider a circular loop of wire lying in the plane of the table. Let the current pass through the loop clockwise. Apply the right-hand rule to find out the direction of the magnetic field inside and outside the loop.
Answer: Using the right-hand rule, curl your fingers in the direction of current; your thumb points in the direction of the magnetic field. Inside the loop, the magnetic field is directed downward, and outside the loop, it is directed upward.
Q2. The magnetic field in a given region is uniform. Draw a diagram to represent it.
Answer:
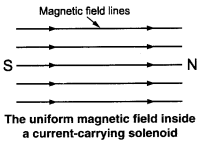
Q3. Choose the correct option.
The magnetic field inside a long straight solenoid carrying current: (a) is zero.
(b) decreases as we move towards its end.
(c) increases as we move towards its end.
(d) is the same at all points.
Answer: (d) is the same at all points.
📝PAGE 231-232
Q1. Which of the following property of a proton can change while it moves freely in a magnetic field? (There may be more than one correct answer.) (a) mass
(b) speed
(c) velocity
(d) momentum
Answer: (c) velocity, (d) momentum
Q2. In Activity 13.7, how do we think the displacement of rod AB will be affected if:
(i) current in rod AB is increased
(ii) a stronger horse-shoe magnet is used
(iii) length of the rod AB is increased
Answer: In all three cases, the force on the rod will increase, hence displacement will be more.
Q3. A positively-charged particle (alpha-particle) projected towards west is deflected towards north by a magnetic field. The direction of magnetic field is: (a) towards south
(b) towards east
(c) downward
(d) upward
Answer: (d) upward
📝PAGE 233
Q1. State Fleming’s left-hand rule.
Answer: If the thumb, forefinger and middle finger of the left hand are stretched mutually perpendicular to each other, and if the forefinger points in the direction of magnetic field and the middle finger in the direction of current, then the thumb will point in the direction of force or motion.
Q2. What is the principle of an electric motor?
Answer: An electric motor works on the principle that a current-carrying conductor placed in a magnetic field experiences a force.
Q3. What is the role of the split ring in an electric motor?
Answer: The split ring reverses the direction of current in the coil every half rotation, ensuring that the motor continues to rotate in the same direction.
📝PAGE 236
Q1. Explain different ways to induce current in a coil.
Answer:
By moving a magnet in or out of the coil.
By moving the coil in a magnetic field.
By changing the magnetic field around a stationary coil.
📝PAGE 237
Q1. State the principle of an electric generator.
Answer: An electric generator works on the principle of electromagnetic induction. When a coil rotates in a magnetic field, an induced current is produced.
Q2. Name some sources of direct current.
Answer: Cells, batteries, solar panels.
Q3. Which sources produce alternating current?
Answer: Power plants, alternators, generators.
Q4. Choose the correct option.
A rectangular coil of copper wires is rotated in a magnetic field. The direction of the induced current changes once in each:
(a) two revolutions
(b) one revolution
(c) half revolution
(d) one-fourth revolution
Answer: (c) half revolution
📝PAGE 238
Q1. Name two safety measures commonly used in electric circuits and appliances.
Answer:
Electric fuse
Earth wire
Q2. An electric oven of 2 kW power rating is operated in a domestic electric circuit (220 V) that has a current rating of 5 A. What result do you expect? Explain.
Answer: Current drawn = Power / Voltage = 2000 / 220 ≈ 9.09 A, which is more than 5 A. Hence, the fuse will blow and the circuit will break due to overloading.
Q3. What precaution should be taken to avoid the overloading of domestic electric circuits?
Answer:
To avoid the overloading of domestic electric circuits, the following precautions should be taken :
(i) The wires used in the circuit must be coated with good insulating materials like PVC, etc.
(ii) The circuit must be divided into different sections and a safety fuse must be used in each section.
(iii) High power appliances like air-conditioner, refrigerator, a water heater, etc. should not be used simultaneously.
SEBA Class 10 Science Chapter 13 – Magnetic Effects of Electric Current Textbook Exercise Questions & Solutions | 2026–27
Q1. Which of the following correctly describes the magnetic field near a long straight wire?
(a) The field consists of straight lines perpendicular to the wire.
(b) The field consists of straight lines parallel to the wire.
(c) The field consists of radial lines originating from the wire.
(d) The field consists of concentric circles centred on the wire.
Answer: (d)
Q2. The phenomenon of electromagnetic induction is:
(a) the process of charging a body.
(b) the process of generating magnetic field due to a current passing through a coil.
(c) producing induced current in a coil due to relative motion between a magnet and the coil.
(d) the process of rotating a coil of an electric motor.
Answer: (c)
Q3. The device used for producing electric current is called a:
(a) generator
(b) galvanometer
(c) ammeter
(d) motor
Answer: (a)
Q4. The essential difference between an AC generator and a DC generator is that:
(a) AC generator has an electromagnet while a DC generator has permanent magnet.
(b) DC generator will generate a higher voltage.
(c) AC generator will generate a higher voltage.
(d) AC generator has slip rings while the DC generator has a commutator.
Answer: (d)
Q5. At the time of short circuit, the current in the circuit:
(a) reduces substantially.
(b) does not change.
(c) increases heavily.
(d) vary continuously.
Answer: (c)
Q6. State whether the following statements are true or false.
(a) An electric motor converts mechanical energy into electrical energy. False
(b) An electric generator works on the principle of electromagnetic induction. True
(c) The field at the centre of a long circular coil carrying current will be parallel straight lines. True
(d) A wire with a green insulation is usually the live wire of an electric supply. False
Q7. List two methods of producing magnetic fields.
Answer:
Using a current-carrying straight conductor
Using a solenoid
Q8. How does a solenoid behave like a magnet? Can you determine the north and south poles of a current–carrying solenoid with the help of a bar magnet? Explain.
Answer: A solenoid behaves like a bar magnet with a north and south pole. Yes, by bringing a bar magnet near the solenoid, we can determine the poles using attraction or repulsion.
Q9. When is the force experienced by a current–carrying conductor placed in a magnetic field largest?
Answer: When the conductor is placed perpendicular to the magnetic field.
Q10. Imagine that you are sitting in a chamber with your back to one wall. An electron beam, moving horizontally from back wall towards the front wall, is deflected by a strong magnetic field to your right side. What is the direction of magnetic field?
Answer: Using Fleming’s Left-Hand Rule, the magnetic field is directed downward.
Q11. Draw a labelled diagram of an electric motor. Explain its principle and working. What is the function of a split ring in an electric motor?
Answer:
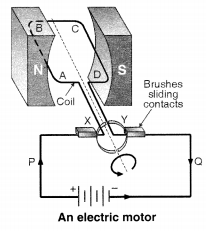
Principle of an Electric Motor: An electric motor works on the principle that a current-carrying conductor placed in a magnetic field experiences a force. This force can produce rotational motion when arranged properly.
Working of an Electric Motor:
- When electric current flows through the coil placed between the poles of a magnet, the two sides of the coil experience forces in opposite directions.
- This happens due to interaction between the magnetic field of the magnet and the magnetic field produced by the current in the coil.
- As a result, the coil starts rotating.
- After half a rotation, the direction of current in the coil must reverse to keep it rotating in the same direction. This is where the split ring comes in.
Function of a Split Ring:
The split ring in an electric motor acts as a commutator. Its main functions are:
- It reverses the direction of current in the coil after every half rotation.
- This ensures that the coil keeps rotating in the same direction continuously.
- Without the split ring, the motor would stop after half a turn as the direction of the force would reverse.
Q12. Name some devices in which electric motors are used.
Answer: Fans, refrigerators, washing machines, mixers, computers.
Q13. A coil of insulated copper wire is connected to a galvanometer. What will happen if:
(i) a bar magnet is pushed into the coil – Galvanometer shows deflection.
(ii) withdrawn – Deflection in opposite direction.
(iii) held stationary – No deflection.
Q14. Two circular coils A and B are placed close to each other. If the current in coil A is changed, will some current be induced in coil B? Give reason.
Answer: Yes, due to electromagnetic induction. The change in magnetic field due to coil A induces current in coil B.
Q15. State the rule to determine the direction of:
(i) Magnetic field around a straight conductor – Right-hand thumb rule: If the current carrying conductor is held in the right hand such that the thumb points in the direction of the current, then the direction of the curl of the fingers will give the direction of the magnetic field.
(ii) Force on a conductor in magnetic field – Fleming’s left-hand rule : Current Stretch the forefinger, the central finger and the thumb of the left hand mutually perpendicular to each other. If the forefinger points in the direction of the magnetic field, the middle finger in the direction of current, then the thumb points in the direction of force in the conductor.
(iii) Induced current – Fleming’s right-hand rule : Stretch the thumb, forefinger and the central finger of the right hand mutually perpendicular to each other. If the forefinger points in the direction of magnetic field, thumb in the direction of motion of the conductor, then the middle finger points in the direction of current induced in the conductor.
Q16. Explain the principle and working of an electric generator with diagram. What is the function of brushes?
Answer:
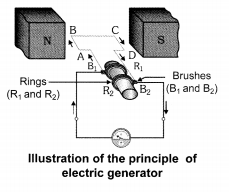
Working of an Electric Generator: When the armature coil ABCD rotates between the poles of a magnet, it cuts the magnetic field lines. This motion causes a change in the magnetic flux linked with the coil, which produces an induced electromotive force (emf) due to electromagnetic induction.
The direction of the induced current is determined using Fleming’s Right-Hand Rule.
- In the first half of the rotation, the current flows in one direction (say through brush B1).
- In the second half, the direction of current reverses and flows through brush B2.
- This cycle continues as the coil keeps rotating.
Hence, the electric current generated is alternating current (AC).
Function of Brushes: The brushes are in contact with the slip rings. Their main role is to transfer the induced current from the rotating coil to the external circuit, making the current available for external use.
Q17. When does an electric short circuit occur?
Answer: When the live wire touches the neutral wire directly, allowing a large current to flow.
Q18. What is the function of an earth wire? Why is it necessary to earth metallic appliances?
Answer: Earth wire protects from electric shock by transferring excess charge to the ground. Earthing ensures user safety in case of insulation failure
It is necessary to earth metallic appliances because it ensures that if there is any current leakage in the metallic cover, the potential of the appliance becomes equal to that of the earth. The potential of the earth is zero. As a result, the person handling the appliance will not get an electric shock.
🎓 About Assam Eduverse
Assam Eduverse is the best educational platform in Assam, offering SEBA, AHSEC (ASSEB), SCERT, CBSE, and Assam Board Solutions along with study materials, notes, and exam preparation guides to help students learn smarter and score higher.
Our expert-prepared answers and MCQs follow the latest Assam Board Syllabus and NCERT Syllabus. We make learning simple, accessible, and effective for all students preparing for board or competitive exams.📘 Visit Assam Eduverse for free Assam Board Solutions, notes, and Study Materials prepared by experts.
