SEBA Class 10 Geography Chapter 4 MCQs – Geography of Assam (2026–27)
SEBA Class 10 Geography Chapter 4 MCQs Geography of Assam (2026–27) are carefully prepared by Assam Eduverse to help HSLC students score higher in Geography objective questions. As per the latest HSLC exam pattern, 45 MCQs are asked, making SEBA Class 10 Geography Chapter 4 MCQs Geography of Assam a highly scoring chapter in Geography.
This Geography chapter explains the physical features of Assam, including location, physiography, climate, rivers, soil, and natural vegetation. The SEBA Class 10 Geography Chapter 4 MCQs Geography of Assam focus on Brahmaputra and Barak valleys, hills, rainfall, and regional divisions, which are frequently asked in HSLC examinations.
By practising these Class 10 SEBA Geography MCQ practice questions, students can improve map-based understanding, concept clarity, and exam confidence. This page also includes HSLC Geography Chapter 4 MCQs previous year questions along with extra objective questions for complete preparation for the HSLC 2026–27 Geography examination.
SEBA HSLC Class 10 Geography Chapter 4 MCQs – Geography of Assam (45 MCQs Pattern)
Table of Contents
A. Previous Year MCQs Questions with Answers
Q.1 According to Census of India, 2001 what percentage of India’s population lived in Assam? [HSLC 2011]
(a) 2.39%
(b) 2.79%
(c) 2.59%
(d) 3.29%
Answer: (c) 2.59%
Q.2 In respect of area, the largest district of Assam is— [HSLC 2012]
(a) Kokrajhar
(b) Nagaon
(c) Karbi Anglong
(d) Cachar
Answer: (c) Karbi Anglong
Q.3 The National Highway (NH) that connects Guwahati with Shillong is— [HSLC 2015; 2017]
(a) NH 52
(b) NH 40
(c) NH 37
(d) NH 31
Answer: (b) NH 40
Q.4 At present, the total number of National Parks including Kaziranga in Assam is— [HSLC 2018]
(a) 10
(b) 7
(c) 20
(d) 6
Answer: (b) 7
Q.5 According to Census of India, 2011 what percentage of India’s population live in Assam? [HSLC 2023]
(a) 2.39%
(b) 2.79%
(c) 2.60%
(d) 3.6%
Answer: (c) 2.60%
Q.6 The first stream of human migration of Assam was— [HSLC 2023]
(a) The Austric group of people
(b) The Tibeto-Burman language speaking Mongoloids
(c) The Ahoms
(d) The Koch Rajbongshis
Answer: (a) The Austric group of people
Q.7 As per the Census of India, 2011, what was the literacy rate of Assam? [HSLC 2024]
(a) 63.25%
(b) 72.19%
(c) 87.10%
(d) 85.90%
Answer: (b) 72.19%
Q.8 As per the 2011 Census report, the first-class towns of Assam having highest to gradually less population are— [HSLC 2024]
(a) Guwahati, Silchar, Dibrugarh, Jorhat
(b) Guwahati, Silchar, Jorhat, Dibrugarh
(c) Guwahati, Silchar, Dibrugarh, Nagaon
(d) Guwahati, Dibrugarh, Silchar, Jorhat
Answer: (a) Guwahati, Silchar, Dibrugarh, Jorhat
Q.9 The first, second and third largest tribes of Assam on the basis of population size are respectively— [HSLC 2024]
(a) The Mishings, The Bodos, The Karbis
(b) The Bodos, The Mishings, The Karbis
(c) The Karbis, The Mishings, The Bodos
(d) The Bodos, The Karbis, The Mishings
Answer: (b) The Bodos, The Mishings, The Karbis
Q.10 The longest National Highway in Assam is— [HSLC 2024]
(a) National Highway 31
(b) National Highway 37
(c) National Highway 52
(d) National Highway 54
Answer: (b) National Highway 37
Q.11 Which is the largest agro-based industry in Assam? [HSLC 2024]
(a) Rubber industry
(b) Silk industry
(c) Paper industry
(d) Tea industry
Answer: (d) Tea industry
Q.12 Arrange the chronological flow of migration of the following groups of people to Assam. [HSLC 2025]
(i) Mongoloid
(ii) Austric
(iii) Aryan
(iv) Ahom
(a) (i), (ii), (iii), (iv)
(b) (ii), (iii), (i), (iv)
(c) (i), (iv), (iii), (ii)
(d) (ii), (i), (iii), (iv)
Answer: (d) (ii), (i), (iii), (iv)
Q.13 During which of the following decades did the State of Assam witness lower growth rate of population as compared to India? [HSLC 2025]
(a) 1901–1911
(b) 1981–1991
(c) 1991–2001
(d) 1941–1951
Answer: (c) 1991–2001
B. Extra HSLC Pattern MCQs Questions with Answers
Q.1 Assam is called the gateway of North-East India because—
(a) It has the largest population
(b) It is centrally located
(c) North-East India is connected with India through Assam
(d) It has maximum transport facilities
Answer: (c) North-East India is connected with India through Assam
Q.2 Assam is connected with the rest of India through a narrow land corridor of about—
(a) 20 km
(b) 30 km
(c) 50 km
(d) 70 km
Answer: (c) 50 km
Q.3 Assam covers about what percentage of India’s total geographical area?
(a) 1.8%
(b) 2.0%
(c) 2.4%
(d) 3.2%
Answer: (c) 2.4%
Q.4 According to Census 2011, the total population of Assam was—
(a) 2.66 crore
(b) 3.12 crore
(c) 3.52 crore
(d) 2.98 crore
Answer: (b) 3.12 crore
Q.5 The sex ratio of Assam as per Census 2011 was—
(a) 935
(b) 948
(c) 958
(d) 970
Answer: (c) 958
Q.6 Which one of the following showed a decline between 2001 and 2011 in Assam?
(a) Literacy rate
(b) Urban population
(c) Rural population
(d) Sex ratio
Answer: (c) Rural population
Q.7 Which city is the most populous urban centre of Assam?
(a) Silchar
(b) Dibrugarh
(c) Jorhat
(d) Guwahati
Answer: (d) Guwahati
Q.8 Which town is the most populous among the second-class towns of Assam?
(a) Diphu
(b) Dhubri
(c) Goalpara
(d) Karimganj
Answer: (b) Dhubri
Q.9 Population growth takes place mainly due to—
(a) Birth rate only
(b) Death rate only
(c) Birth rate, death rate and migration
(d) Natural calamities
Answer: (c) Birth rate, death rate and migration
Q.10 The highest decadal population growth rate in Assam was recorded during—
(a) 1901–1911
(b) 1931–1941
(c) 1951–1961
(d) 1981–1991
Answer: (c) 1951–1961
Q.11 Which valley accommodates about 85% of Assam’s population?
(a) Barak Valley
(b) Upper Brahmaputra Valley
(c) Hill Region
(d) Brahmaputra Valley
Answer: (d) Brahmaputra Valley
Q.12 Population density in Assam as per Census 2011 was—
(a) 340 persons per km²
(b) 398 persons per km²
(c) 420 persons per km²
(d) 470 persons per km²
Answer: (b) 398 persons per km²
Q.13 The most densely populated district of Assam as per 2011 Census is—
(a) Nagaon
(b) Kamrup (Metro)
(c) Dhubri
(d) Barpeta
Answer: (b) Kamrup (Metro)
Q.14 The least densely populated district of Assam is—
(a) Karbi Anglong
(b) Kokrajhar
(c) Dima Hasao
(d) Dhemaji
Answer: (c) Dima Hasao
Q.15 The main cause of population growth in Assam is—
(a) High birth rate
(b) Low death rate
(c) Migration
(d) Urbanisation
Answer: (c) Migration
Q.16 Match Column A with Column B and choose the correct answer:
Column A
(i) Austric group
(ii) Mongoloid group
(iii) Aryan group
(iv) Ahoms
Column B
(a) Came from Shan Plateau
(b) First human stream
(c) Indo-Aryan language speakers
(d) Tibeto-Burman language speakers
Options:
(a) (i-b), (ii-d), (iii-c), (iv-a)
(b) (i-d), (ii-b), (iii-a), (iv-c)
(c) (i-c), (ii-d), (iii-b), (iv-a)
(d) (i-b), (ii-c), (iii-d), (iv-a)
Answer: (a) (i-b), (ii-d), (iii-c), (iv-a)
Q.17 Assertion (A): Migration has played a major role in Assam’s population growth.
Reason (R): Birth and death rates of Assam are much higher than national average.
(a) Both A and R are correct
(b) A is correct, R is incorrect
(c) A is incorrect, R is correct
(d) Both A and R are incorrect
Answer: (b) A is correct, R is incorrect
Q.18 Assertion (A): Barak Valley has high population density.
Reason (R): It has fertile alluvial plains and good transport facilities.
(a) Both A and R are correct
(b) A is correct, R is incorrect
(c) A is incorrect, R is correct
(d) Both A and R are incorrect
Answer: (a) Both A and R are correct
Q.19 Arrange the following valleys of Assam in increasing order of population density:
Q.19 Arrange the following valleys of Assam in increasing order of population density:
(i) Upper Brahmaputra Valley
(ii) Middle Brahmaputra Valley
(iii) Lower Brahmaputra Valley
Options:
(a) (i), (ii), (iii)
(b) (ii), (i), (iii)
(c) (iii), (ii), (i)
(d) (i), (iii), (ii)
Answer: (a) (i), (ii), (iii)
Q.20 Which of the following are causes of population growth in Assam?
(i) Migration
(ii) Decrease in death rate
(iii) Industrialisation
(iv) Urban planning
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (i) and (iii)
(c) (ii) and (iv)
(d) (iii) and (iv)
Answer: (a) (i) and (ii)
Q.21 Road transport is suitable mainly for—
(a) Long-distance transport
(b) Short-distance transport
(c) International transport
(d) Air connectivity
Answer: (b) Short-distance transport
Q.22 Which is the railway zone under which Assam falls?
(a) Eastern Railway
(b) North-East Frontier Railway
(c) Northern Railway
(d) East Central Railway
Answer: (b) North-East Frontier Railway
Q.23 The Brahmaputra river was declared as National Waterway No.—
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 5
(d) 6
Answer: (b) 2
Q.24 Lokapriya Gopinath Bordoloi International Airport is located at—
(a) Tezpur
(b) Jorhat
(c) Guwahati
(d) Silchar
Answer: (c) Guwahati
Q.25 Which of the following is a non-renewable resource of Assam?
(a) Forest
(b) Water
(c) Mineral oil
(d) Wildlife
Answer: (c) Mineral oil
Q.26 The most important soil for agriculture in Assam is—
(a) Laterite soil
(b) Hill soil
(c) Alluvial soil
(d) Piedmont soil
Answer: (c) Alluvial soil
Q.27 Which forest type is most widespread in Assam?
(a) Tropical dry deciduous
(b) Tropical evergreen
(c) Reverine forest
(d) Thorn forest
Answer: (b) Tropical evergreen
Q.28 The oldest oil field of India is—
(a) Naharkatia
(b) Moran
(c) Digboi
(d) Rudrasagar
Answer: (c) Digboi
Q.29 The principal crop of Assam is—
(a) Wheat
(b) Tea
(c) Rice
(d) Jute
Answer: (c) Rice
Q.30 Which rice is most extensively cultivated in Assam?
(a) Autumn rice
(b) Winter rice
(c) Summer rice
(d) Bodo rice
Answer: (b) Winter rice
Q.31 Jhum cultivation is mainly practised in—
(a) Barak Valley
(b) Brahmaputra Valley
(c) Karbi Anglong and Dima Hasao
(d) North Bank Plain
Answer: (c) Karbi Anglong and Dima Hasao
Q.32 Assam produces more than 50% of India’s—
(a) Rubber
(b) Tea
(c) Silk
(d) Rice
Answer: (b) Tea
Q.33 Muga silk is also known as—
(a) White silk
(b) Pat silk
(c) Golden silk
(d) Raw silk
Answer: (c) Golden silk
Q.34 Which industry employs the largest number of people in Assam?
(a) Tea industry
(b) Oil industry
(c) Silk industry
(d) Paper industry
Answer: (a) Tea industry
Q.35 One major cause of degradation of natural resources in Assam is—
(a) Low rainfall
(b) Population pressure
(c) Volcanic activity
(d) Earthquakes
Answer: (b) Population pressure
Q.36 Assam’s economy mainly depends on—
(a) Industry
(b) Trade
(c) Agriculture
(d) Mining
Answer: (c) Agriculture
Q.37 The hill region of Assam has—
(a) Dense population
(b) Moderate population
(c) Sparse population
(d) Urban population
Answer: (c) Sparse population
Q.38 The Barak Valley population density is high mainly because of—
(a) Mining activities
(b) Fertile plains
(c) Tea cultivation
(d) Industrialisation
Answer: (b) Fertile plains
Q.39 The youth population of Assam (15–34 years) forms about—
(a) 20%
(b) 25%
(c) 35%
(d) 50%
Answer: (c) 35%
Q.40 The largest agro-based industry of Assam is—
(a) Rubber industry
(b) Silk industry
(c) Paper industry
(d) Tea industry
Answer: (d) Tea industry
Q.41 Assam produces about what percentage of India’s natural gas?
(a) 10%
(b) 15%
(c) 25%
(d) 40%
Answer: (c) 25%
Q.42 Which mineral is known as ‘liquid gold’ in Assam?
(a) Coal
(b) Natural gas
(c) Mineral oil
(d) Limestone
Answer: (c) Mineral oil
Q.43 Which district is rich in coal deposits?
(a) Karimganj
(b) Tinsukia
(c) Barpeta
(d) Nalbari
Answer: (b) Tinsukia
Q.44 The number of agro-climatic zones in Assam is—
(a) Four
(b) Five
(c) Six
(d) Seven
Answer: (c) Six
Q.45 The most important factor for human resource development is—
(a) Migration
(b) Education
(c) Urbanisation
(d) Industrial growth
Answer: (b) Education
Q.46 Which sector contributes least to Assam’s economy?
(a) Agriculture
(b) Industry
(c) Service sector
(d) Transport
Answer: (b) Industry
Q.47 Flood affects Assam mainly due to—
(a) Earthquakes
(b) Heavy rainfall and rivers
(c) Deforestation only
(d) Cyclones
Answer: (b) Heavy rainfall and rivers
Q.48 Which crop is cultivated mainly on floodplains?
(a) Wheat
(b) Jute
(c) Tea
(d) Sugarcane
Answer: (b) Jute
Q.49 The main occupation of people in Assam is—
(a) Trade
(b) Industry
(c) Agriculture
(d) Transport
Answer: (c) Agriculture
Q.50 Sustainable development means—
(a) Maximum exploitation of resources
(b) No use of resources
(c) Proper use and conservation of resources
(d) Industrial expansion only
Answer: (c) Proper use and conservation of resources
C. Previous Year Short Type Questions with Answers
Q.1. What are the principal aims of the Industrial and Investment Policy of Assam Government announced in 2014? [HSLC 2019]
Answer: The principal aims of the Industrial and Investment Policy of Assam Government announced in 2014 are-
- To increase the Gross Domestic Product of the state by developing manufacturing and service sectors.
- To increase per capita income and generate employment opportunities, especially in rural areas.
- To encourage investment for development of micro, small and medium industries.
- To create a large number of skilled personnel.
Q.2. Mention the advantages of water transport system in Assam. [HSLC 2019]
Answer: The advantages of water transport system in Assam are-
- Assam is a land of rivers, so there is wide scope for expansion.
- It is cheaper as fuel cost is less.
- Suitable for carrying heavy goods.
- Causes less air pollution.
- Helpful during floods and natural disasters.
Q.3. Analyze briefly the causes responsible for growth of population in Assam. [HSLC 2019]
Answer: The causes responsible for growth of population in Assam are-
- Natural growth due to birth rate exceeding death rate.
- Large scale migration from Bangladesh and other states.
- Decrease in death rate due to modern medical facilities.
Migration has contributed more significantly to population growth.
Q.4. Mention the major causes which are regarded as hindrance to the development of transport system of Assam. [HSLC 2019]
Answer: The major causes which are regarded as hindrance to the development of transport system of Assam are-
Varied topography like hills, plateaus and wetlands.
- Narrow corridor connection with mainland India.
- Heavy rainfall damages roads.
- Lack of coordination among road, rail, water and air transport.
- Underdeveloped industrial base and limited markets.
Q.5. Mention four mineral resources of Assam. [HSLC 2020]
Answer: Four mineral resources of Assam are-
- Coal
- Mineral oil
- Natural gas
- Limestone
Q.6. Mention two plain tribes and two hill tribes of Assam. [HSLC 2020]
Answer: Two plain tribes—
- Bodo
- Mishing
Two hill tribes—
- Karbi
- Dimasa Kachari
Q.7. Mention three problems of economic development in Assam. [HSLC 2020]
Answer: Three problems of economic development in Assam are-
- Underdeveloped transport and communication system.
- Lack of sufficient capital and industrial investment.
- Slow growth of agro-based and industrial sectors.
Q.8. Write a note on population distribution in Assam. [HSLC 2020]
Answer: Population distribution in Assam is uneven. About 85% of the population lives in the Brahmaputra Valley due to fertile plains and favourable conditions. The Barak Valley is also densely populated because of fertile alluvial soils. On the other hand, the hill region comprising Karbi Anglong and Dima Hasao has sparse population due to inconvenient physiographic conditions.
Q.9. Write the names of the States and Countries that surround the State of Assam. [HSLC 2022]
Answer: States surrounding Assam are-
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Nagaland
- Manipur
- Mizoram
- Meghalaya
- Tripura
- West Bengal
Countries surrounding Assam—
- Bhutan
- Bangladesh
Q.10. Briefly describe the mineral resources of Assam. [HSLC 2022]
Answer: Assam is rich in mineral resources such as coal, mineral oil, natural gas and limestone. Digboi is the oldest oil field of India. Major oil fields include Naharkatia, Moran, Rudrasagar and Lakowa. Coal is found mainly in Tinsukia and Dibrugarh districts. Limestone is found in Karbi Anglong and Dima Hasao districts.
D. Previous Year Essay Type Questions with Answers
Q.11. Briefly discuss the agricultural activities of the hill region of Assam. [HSLC 2011]
Answer: The hill region comprising Karbi Anglong and Dima Hasao is mainly characterised by jhum cultivation (shifting cultivation). The tribal people practise jhum by clearing and burning forest on hill slopes. After a few years, when soil fertility declines, they shift to another plot. Fruits are also cultivated on suitable hill slopes and rice is grown in narrow river plains. However, jhum cultivation causes problems like soil erosion and deforestation.
Q.12. Discuss the Agricultural activities of the hilly region of Assam. [HSLC 2016]
Answer: Agriculture in the hilly region is dominated by jhum cultivation. About 66% area of Karbi Anglong and 85% of Dima Hasao are hilly. Tribal people practise shifting cultivation by traditional methods. Mixed crops are grown but production is low. Environmental problems like soil erosion and forest destruction arise. Terrace cultivation is suggested as an alternative.
Q.13. Write a brief note on the potentialities of tourism industry of Assam. [HSLC 2016]
Answer: Assam has great potential for tourism due to its natural beauty, wildlife, national parks, tea gardens and cultural diversity. Kaziranga National Park, Manas National Park and other wildlife sanctuaries attract tourists. Historical monuments and river landscapes add to tourism prospects. Proper infrastructure and investment can develop tourism further.
Q.14. Name the major minerals of Assam. Explain briefly the oil fields of Assam. [HSLC 2017]
Answer: Major minerals are coal, mineral oil, natural gas and limestone.
Digboi is the oldest oil field of India. Other major oil fields are Naharkatia, Moran-Hugrijan, Rudrasagar, Lakowa, Geleki and Amaguri. Oil is refined in Digboi, Guwahati, Bongaigaon and Numaligarh refineries.
Q.15. What are the major agro-based industries of Assam? Explain briefly about tea industry of Assam. [HSLC 2017]
Answer: Major agro-based industries are tea, silk, rubber, food processing, forestry and paper industry.
Tea industry is the largest agro-based industry of Assam. Assam produces more than half of India’s total tea. Tea is cultivated in about 318 thousand hectares of land. Over 6.86 lakh people are engaged in this industry.
Q.16. Give four reasons why industrial development is still very slow in Assam. [HSLC 2018]
Answer: Four reasons why industrial development is still very slow in Assam are-
- Lack of integrated planning.
- Underdeveloped transport and communication.
- Insufficient capital investment.
- Insurgency and social unrest.
Q.17. Mention any four problems of tourism in Assam. [HSLC 2018]
Answer: Four problems of tourism in Assam are-
- Inadequate capital investment.
- Poor transport system.
- Lack of proper infrastructure at tourist spots.
- Lack of environment to attract foreign tourists.
Q.18. Mention the different streams of human migration into Assam sequentially since the ancient times to the present. [HSLC 2018]
Answer:
- Austric group
- Tibeto-Burman Mongoloid group
- Indo-Aryan group
- Ahoms
- Muslim settlers
- British period migrants (tea tribes, Nepalis, Bengalis, etc.)
Q.19. Discuss briefly the causes responsible for variation in the distribution of population in Assam with suitable examples. [HSLC 2018, 2023]
Answer: Population distribution varies due to physical and economic factors. Fertile plains of Brahmaputra and Barak valleys have dense population. The hill region has sparse population due to rugged terrain. Developed transport and economic opportunities increase population density in certain districts like Kamrup (Metro).
Q.20. Narrate the causes responsible for degradation of natural resources of Assam. [HSLC 2019]
Answer: The causes responsible for degradation of natural resources of Assam are-
- Rapid population growth.
- Expansion of settlements and agriculture.
- Deforestation.
- Excessive use of chemical fertilizers.
- Unplanned urbanisation and industrialisation.
Q.21. Describe briefly the agro-based industries of Assam. [HSLC 2019/2020]
Answer: Agro-based industries include tea, silk, rubber, food processing and paper industries. Tea is the largest industry. Silk industry produces Eri, Muga and Pat silk. Rubber plantation is increasing. Food processing industries are developing based on fruits and vegetables.
Q.22. Discuss the role of agriculture in the economy of Assam. [HSLC 2020]
Answer: About 75% of the population depends on agriculture. More than 53% of working population is engaged in agriculture. Rice is the principal crop. Agriculture forms the backbone of Assam’s economy and supports agro-based industries like tea and silk.
Q.23. Write an account on railway transport development in Assam. [HSLC 2020]
Answer: Railway transport in Assam comes under North-East Frontier Railway with headquarters at Maligaon, Guwahati. Total rail length was about 2458.93 km. Railways connect almost all districts and help in economic development by transporting goods and passengers.
Q.24. Discuss the factors of industrial backwardness in Assam. [HSLC 2020/2024]
Answer: The factors of industrial backwardness in Assam are-
- Lack of integrated planning.
- Poor transport and communication.
- Insufficient capital and investment.
- Inadequate power supply.
- Insurgency problems.
Q.25. Mention the problems of agricultural development in Assam. [HSLC 2023]
Answer: The problems of agricultural development in Assam are-
- Traditional farming methods.
- Fragmented land holdings.
- Frequent floods and erosion.
- Lack of irrigation facilities.
- Poor storage and marketing facilities.
Q.26. Write briefly about the water resources of Assam. [HSLC 2024]
Answer: Assam is rich in surface and groundwater resources. The Brahmaputra and Barak rivers and their tributaries carry about one-third of India’s water resources. There are more than three thousand wetlands. These water resources are used for agriculture, transport, industry and domestic purposes, though not fully utilised.
Q.27. Mention five major causes which are regarded as hindrance to the development of transport system of Assam. [HSLC 2024]
Answer: Five major causes which are regarded as hindrance to the development of transport system of Assam are-
- Difficult topography.
- Narrow corridor connection.
- Heavy rainfall damaging roads.
- Underdeveloped industry.
- Lack of coordination among transport sectors.
Q.28. What are the causes responsible for degradation of the natural resources of Assam? [HSLC 2024]
Answer: The causes responsible for degradation of the natural resources of Assam are-
- Rapid population growth.
- Expansion of human settlements.
- Deforestation.
- Unplanned urbanisation and industrialisation.
- Excessive exploitation of minerals.
Q.29. Does Assam have prospect for the development of water transport? Give four arguments. [HSLC 2024]
Answer: Yes, Assam has great prospects for water transport because—
- It has long navigable rivers like Brahmaputra and Barak.
- Water transport is cheaper and suitable for heavy goods.
- It reduces air pollution.
- It is useful during floods and in remote areas lacking roads.
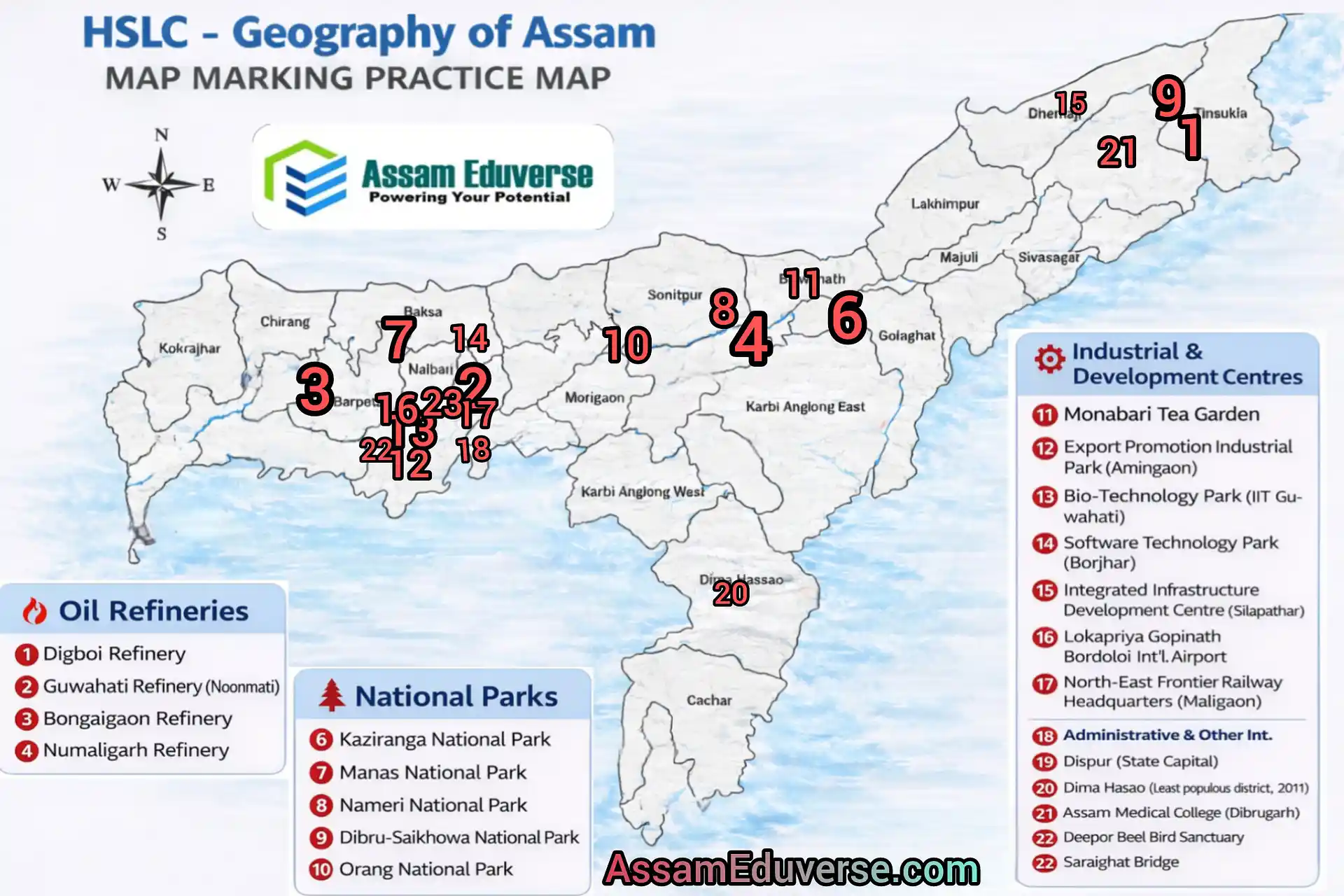
Question. Important places to locate in the map of Assam in Social Science SEBA HSLC Examination.
Answer:
The following places have been frequently asked in HSLC examinations for map location from the chapter Geography of Assam. These should be prepared carefully:
Oil Refineries and Oil Fields
- Digboi Oil Refinery (Oldest oil refinery of India)
- Guwahati Refinery (Noonmati)
- Bongaigaon Refinery
- Numaligarh Refinery
- Digboi Oil Field
National Parks and Wildlife Sanctuaries
- Kaziranga National Park
- A National Park on the south bank of the Brahmaputra
- A National Park of Assam
- A Bird Sanctuary
- National Park where white-winged wood duck is found
Tea Gardens and Agro-based Centres
- Monabari Tea Garden (Largest tea garden of Asia)
- Largest Tea Garden of Asia
Industrial Parks and Centres
- Export Promotion Industrial Park (Amingaon)
- Bio-Technology Park (IIT Guwahati)
- Software Technology Park (Borjhar)
- An Integrated Infrastructure Development Centre (e.g., Silapathar, Dalgaon, Demow, Titabor, etc.)
Transport and Communication
- Lokapriya Gopinath Bordoloi International Airport (Guwahati)
- Head Quarters of North-East Frontier Railway (Maligaon, Guwahati)
- A bridge connecting north and south bank of the Brahmaputra
Mineral and Resource Areas
A Coalfield (e.g., Makum region)
Administrative and Other Important Places
- State Capital (Guwahati/Dispur)
- Least populous district as per Census 2011 (Dima Hasao)
- A Medical College
These are the major locations repeatedly asked in SEBA HSLC Social Science examinations and should be thoroughly practised on the outline map of Assam.
SEBA Class 10 Geography Chapter 4 MCQs – Geography of Assam
SEBA Class 10 Geography Chapter 4 MCQs Geography of Assam are an essential study resource for HSLC students preparing for Geography MCQs. These SEBA Class 10 Geography Chapter 4 MCQs Geography of Assam strictly follow the updated SEBA 2026–27 Geography syllabus and the latest 45 MCQs examination pattern, making SEBA Class 10 Geography Chapter 4 MCQs Geography of Assam highly exam-oriented.
This page includes SEBA Class 10 Geography Chapter 4 MCQs Geography of Assam covering location, physical divisions, river systems, climate, and soil of Assam. The SEBA Class 10 Geography Chapter 4 MCQs Geography of Assam explain the Brahmaputra Valley, Barak Valley, hills, rainfall pattern, and natural vegetation, ensuring SEBA Class 10 Geography Chapter 4 MCQs Geography of Assam remain concept-focused.
Students will also find HSLC Geography Chapter 4 MCQs previous year questions highlighting repeated Geography trends. Regular practice of SEBA Class 10 Geography Chapter 4 MCQs Geography of Assam along with SEBA Geography Chapter 4 objective questions improves map awareness, accuracy, and Geography exam readiness.
If you are searching for reliable and updated SEBA Class 10 Geography Chapter 4 MCQs Geography of Assam, this content prepared by Assam Eduverse will help you revise Assam-specific Geography concepts effectively and score higher using SEBA Class 10 Geography Chapter 4 MCQs Geography of Assam.
FAQs – SEBA Class 10 Geography Chapter 4 MCQs
1. Are these SEBA Class 10 Geography Chapter 4 MCQs based on the latest HSLC exam pattern?
Yes, these SEBA Class 10 Geography Chapter 4 MCQs Geography of Assam follow the latest 45 MCQs HSLC Geography exam pattern.
2. Does this page include HSLC Geography Chapter 4 MCQs previous year questions?
Yes, this page includes HSLC Geography Chapter 4 MCQs previous year along with extra objective questions.
3. Is Geography of Assam important for Geography MCQs?
Yes, Geography of Assam is a very important chapter and MCQs are frequently asked from this topic in HSLC Geography examinations.
4. Are these MCQs useful for Class 10 SEBA Geography exam preparation?
Yes, these SEBA Geography Chapter 4 objective questions are ideal for Geography exam preparation and revision.
5. Are these Geography MCQs chapterwise?
Yes, all SEBA Class 10 Geography Chapter 4 MCQs are strictly chapterwise.
6. Are these MCQs updated for HSLC 2026–27 Geography examination?
Yes, these SEBA Class 10 Geography Chapter 4 MCQs Geography of Assam are fully updated for HSLC 2026–27 Geography exams.
7. Who prepared these Geography Chapter 4 MCQs?
These Geography MCQs are prepared by subject experts of Assam Eduverse following SEBA Geography guidelines.
🎓 About Assam Eduverse
Assam Eduverse is the best educational platform in Assam, offering SEBA, AHSEC (ASSEB), SCERT, CBSE, and Assam Board Solutions along with study materials, notes, and exam preparation guides to help students learn smarter and score higher.
Our expert-prepared answers and MCQs follow the latest Assam Board Syllabus and NCERT Syllabus. We make learning simple, accessible, and effective for all students preparing for board or competitive exams.📘 Visit Assam Eduverse for free Assam Board Solutions, notes, and Study Materials prepared by experts.

Thank you bhaiya bohot kaam aaya hai